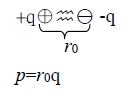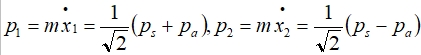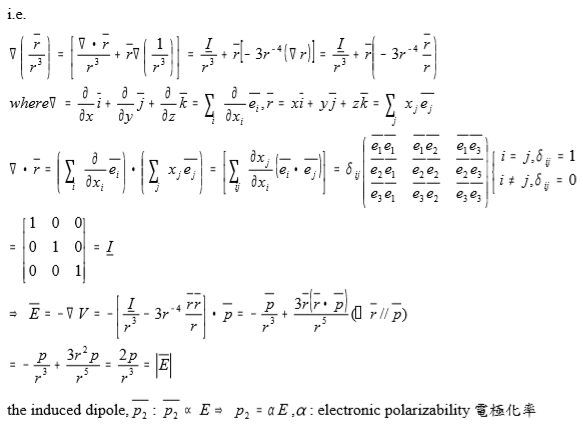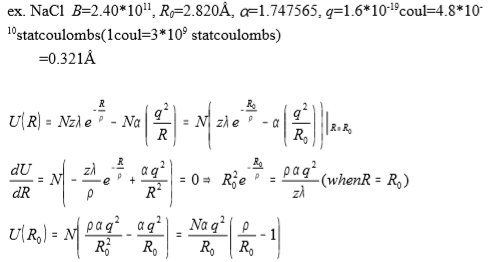字體:小 中 大
字體:小 中 大 |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017/12/13 11:43:31瀏覽541|回應0|推薦0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Chap. 3 Crystal binding Principle types of crystalline binding
Crystal of inert gas 不考慮thermal vibration if –q分布中心在中心,則場效應=0
if thermal vibration at 0K, zero-point energy = ½ℏω=½cu²=½mw²u² u²1/2平均距離, u:位移, c:彈性係數 k binding force in the inert gas crystal at instant t : the interaction energy between two diploes, p₁, p₂, separated by R is given by U(R)=(p₁∙p₂)/R³-3(p₁∙R)(p₂∙R)/R⁵ → U(R)=(p₁∙p₂)/R³-3(p₁∙p₂)/R³=-2(p₁∙p₂)/R³
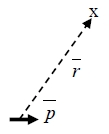
V=p∙R/R³, E=-V=-(p∙R/R³)=-p∙(R/R³)-(R/R³)∙ p p=0, 與電荷密度有關∵r距離太遠
i.e. (R/R³)=[∙R/R³+R(1/R³]=I/R³+R[-3R⁻⁴(R)]=I/R³+R[-3R⁻⁴(R/R)] where =(∂∕∂x)i+(∂∕∂y)j+(∂∕∂z)k=∑ᵢ (∂∕∂xᵢ)eᵢ, r=xi+yj+zk=∑j xj ej , ∙r=[∑ᵢ (∂∕∂xᵢ)eᵢ]∙[∑j xj ej]=[∑ᵢj (∂xj ∕∂xᵢ)(eᵢ∙ej )]=δᵢj =I, i.e. δᵢj=1 if i=j or δᵢj=0 if i≠j E=-V=-[I/R³-3R⁻⁴(R∙R/R)]∙p=-p/r³+3R(R∙p/R⁵)=-p/R³+3R²p/R⁵=2p/R³=|E| ⸪ R// p the induced dipole, p₂ : p₂ E→p₂=αE, : electronic polarizability電極化率
⸫ p₂=α(2p/R³)=2αqr₀/R³ and U(R)=-2(p₁∙p₂)/R³=(-2/R³)∙r₀q∙(2αqr₀/R³) =-4α(r₀q)²/R⁶=-A/R⁶ → F=-U=-dU/dR 1/R⁷ Quantum derivation of van der Waals force
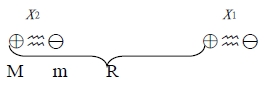
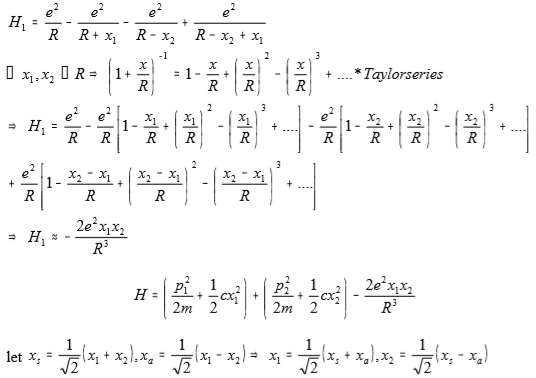
total energy, H=(p₁²/2m+½cx₁²)+(p₂²/2m+½cx₂²)+H₁, H1: 靜電位能 ex. H原子, Eₙ=(n+½)ℏω H₁=e²/R-e²/(r+x₁)-e²/(R-x₂)+e²/(R-x₂+x₁) ⸪ x₁, x₂<<R → (1+R/r)⁻¹=1-x/R+(x/R)²-(x/R)³+... Taylor series H₁=e²/R-e²/R[1-x₁/R+(x₁/R)²-(x₁/R)³+...]-e²/R[1-x₂/R+(x₂/R)²-(x₂/R)³+...]+e²/r[1-(x₂-x₁)/R+(x₂-x₁)²/R²-(x₂-x₁)³/R³+...] → H₁≈-2e²x₁x₂/R³ H=(p₁²/2m+½cx₁²)+(p₂²/2m+½cx₂²)-2e²x₁x₂/R³ let xₛ=1/√2(x₂+x₁), xₐ=1/√2(x₁-x₂) → x₁=1/√2(xₛ+xₐ), x₂=1/√2(xₛ-xₐ)
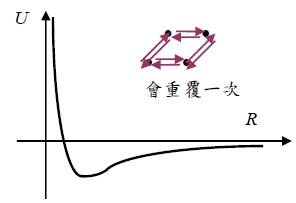
H=(p₁²/2m+½cx₁²)+(p₂²/2m+½cx₂²)-2ex₁x₂/R³ ={[1/√2(pₛ+pₐ)²/2m]+½c[1/√2(xₛ+xₐ)]²}+{[1/√2(pₛ-pₐ)²/2m]+½c[1/√2(xₛ-xₐ)]²}-2e²[1/√2(xₛ+xₐ)][1/√2(xₛ-xₐ)]/R³ =[½(pₛ²+2pₛpₐ+pₐ²+pₛ²-2pₛpₐ+pₐ²)]/2m+c/2[½(xₛ²+2xₛxₐ+xₐ²)+½(xₛ²-2xₛxₐ+xₐ²)]-e²(xₛ²-xₐ²)/R³=pₛ²/2m+pₐ²/2m+½cxₛ²+½cxₐ²-e²(xₛ²-xₐ²)/R³ =[pₛ²/2m+½(c-2e²/R³)xₛ²]+[pₐ²/2m+½(c+2e²/R³)xₐ²] ∵為Simple Harmonic motion Eₙ=(n+½)ℏω₀ if H=H0+H1 H=E (H0+H1)=E H0+H1=E *The zero point energy(n=0) of the system ½ ħ(ωs+ωa)—with dipole-to-dipole interaction, H0+H1(Ep.p.+ E0-0) ½ ħ(ω0+ω0)—without D-D interaction(E0-0) ∆U=½ ħ(ωs+ωa)-½ ħ(ω0+ω0) ω0=(c/m)1/2, ωs=[(c-2e²/R³)/m]1/2=(c/m)1/2[1-½(2e²/cR³)-⅛(2e²/cR³)²+...] ωa=[(c+2e²/R³)/m]1/2=(c/m)1/2[1+½(2e²/cR³)-⅛(2e²/cR³)²+...] → ∆U=½ ħ(ωs+ωa)-½ ħ(ω0+ω0)≈ ½ ħ[ω0+ω0-¼ω0 (2e²/cR³)²]-½ ħ(ω0+ω0) =-ℏω₀/8(2e²/cR³)² Repulsive interaction—due to the overlapping of electron orbit[Pauli exclusion principle] Empirical form B/R¹² the total potential energy of two inert gas atoms at separation R is U(R)=B/R¹²-A/R⁶=4ε[(σ/R)¹²-(σ/R)⁶]
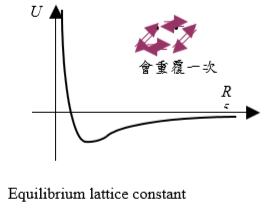
Equilibrium lattice constant Uₜₒₜₐₗ=½∑ᵢ ∑j Uij=½∑j (∑ᵢUij)=(N/2)∑jUij now Uij=4ε[(σ/Rij)¹²-(σ/Rij)⁶ ] let Rij=Pij R → Uij=4ε[(1/Pij)¹²(σ/R)¹²-(1/Pij)⁶(σ/R)⁶] Uₜₒₜₐₗ=½N4ε[∑j(1/Pij)¹²(σ/Rij)¹²-∑j(1/Pij)⁶(σ/Rij)⁶] For inert gas crystal, in addition to He.
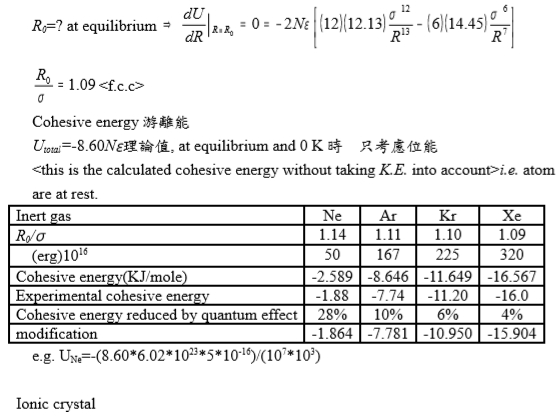
∑j(1/Pij)¹²=12∙1⁻¹²+6∙√2⁻¹²+12∙2⁻¹²+...=12.1388 ∑j(1/Pij)⁶=12∙1⁻⁶+6∙√2⁻⁶+12∙2⁻⁶+...=14.45392 Uₜₒₜₐₗ=2Nε[12.1388(σ/R)¹²-14.45392(σ/R)⁶] R0=? at equilibrium dU/dR|R=R₀=0=-2Nε[12.13(12σ¹² /R¹³)-14.45(6σ⁶/R⁷)] R0/σ=1.09 Cohesive energy游離能 Utotal=-8.60N理論值, at equilibrium and 0 K時, 只考慮位能 K.E. into account>i.e. atom are at rest.
e.g. UNe=-(8.606.021023510-16)/(107103)
Ionic crystal Two common crystal structure: 1. NaCl(f.c.c.), 2. CsCl(b.c.c.) What forces contribute to the crystal binding?
Uₜₒₜₐₗ=½∑ᵢ ∑j Uij, energy includes(i)coulomb: ±q²/rij, (ii)exchange: λe-rij/ρ Uₜₒₜₐₗ=½∙2N∑jUij=N∑jUij=N∑j(λe-rij/ρ±q²/rij) 令rij=PijR, Uₜₒₜₐₗ=N∑jλe-rij/ρ-N∑j(±1/Pij)(q²/R), ∑j(±1/Pij)=Modelung constant Uₜₒₜₐₗ=Nzλe-R/ρ-N∑j(±1/Pij)(q²/R) , define α≡∑j(±1/Pij)=modelung constant NaCl crystal(f.c.c.): pick Cl- as a reference ion Nearest ion: 6Na+, R0 2nd nearest ions: 12 Cl-, √2R0 3rd nearest ion: 8 Na+, √3R0 α=[6∙1⁻¹+12∙√2⁻¹²+8∙√3⁻¹+...]=1.747565 CsCl crystal(b.c.c.) : pick Cs+- as a reference ion Nearest ion: 8Cl-, R0=√3a/2 2nd nearest ions: 6Cs+, R=a=2R0/√3 3rd nearest ion: … α=1.762675 Uₜₒₜₐₗ=Nzλe-R/ρ-Nα(q²/R) determination of , : characteristic force range bulk modulus, B≡-VdP/dV, definition for a crystal of f.c.c. structure V=2NR³ → dV=6NR²dR B=-2NR³dP/(6NR²dR)=-(R/3)(dP/dR) dU=TdS-PdV=-PdV=-P6NR²dR at 0 K and R=R0 P=-(1/6NR²)dU/dR, ⸫ dP/dR=-(1/6NR²)d²U/dR²+(1/3NR³)dU/dR B=-(R/3)(dP/dR)=-(R/3)[-(1/6NR²)d²U/dR²+(1/3NR³)dU/dR] =(1/18NR)d²U/dR²+(1/9NR²)dU/dR] at equilibrium state, R=R0 dU/dR=0, ⸫ B=(1/18NR)d²U/dR²|R=R₀ Uₜₒₜₐₗ=Nzλe-R/ρ-Nα(q²/R) → dU/dR=N[-zλe-R/ρ/ρ+αq²/R²]=0, R0²=ραq²/(zλe-R/ρ) d²U/dR²=N[zλe-R/ρ/ρ²-2αq²/R³]|R=R₀=N[αq²/ρR₀²-2αq²/R₀³] → B=(1/18NR₀)∙N[αq²/ρR₀²-2αq²/R₀³]=αq²/18R₀⁴(R₀/ρ-2) → R₀/ρ=18R₀⁴B/αq²+2, ⸫ ρ=R₀(18R₀⁴B/αq²+2)⁻¹ ex. NaCl B=2.401011, R0=2.820Å, =1.747565, q=1.610-19coul=4.810-10 statcoulombs(1coul=3109 statcoulombs) → =0.321Å
U(R)=Nzλe-R/ρ-Nα(q²/R)=N[zλe-R₀/ρ-α(q²/R₀)]|R=R₀, dU/dR=N[-zλe-R/ρ/ρ+αq²/R²]=0, R0²e-R/ρ=ραq²/(zλ) when R=R0 U(R0)=N[αq²ρ/R₀²-αq²/R₀]=Nαq²/R₀[ρ/R₀-1]
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ( 知識學習|隨堂筆記 ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||



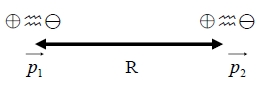
 =
=