字體:小 中 大
字體:小 中 大 |
|
|
|
| 2018/10/21 10:11:03瀏覽1087|回應0|推薦0 | |
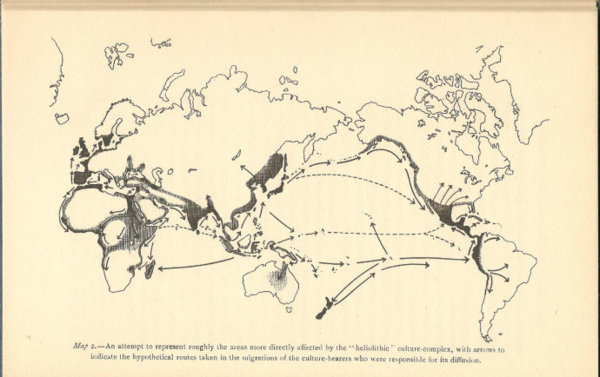
智人的遠古遷徙圖
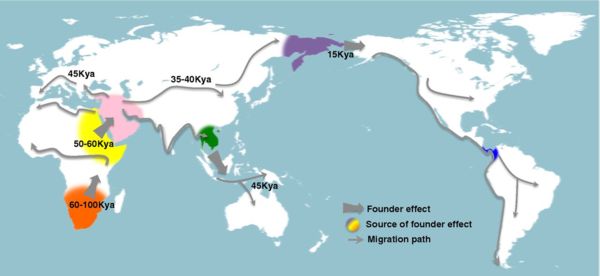
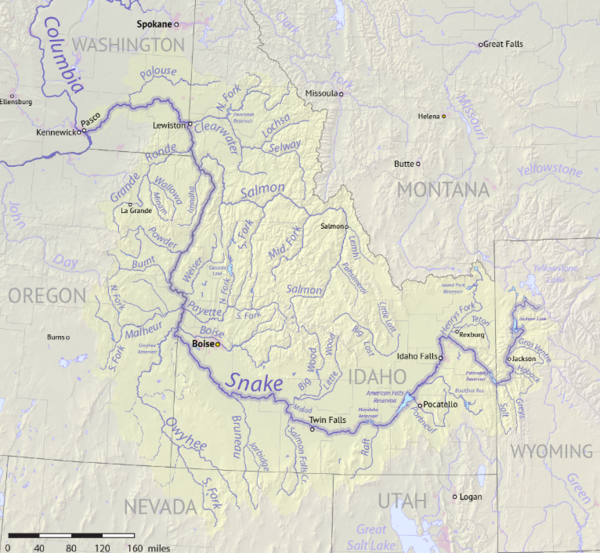
Ancient dispersal patterns of modern humans during the past 100,000 y. 這圖沒有中國部分。而且往美洲的來源也不同。 如果一群人走白令大陸(Beringia)沿海岸來到美洲,當然是想要早點進入內陸,離開洶湧的大海,自然當它們來到Oregan 發現了 Columbia River 出海口,自然就會溯河而上,經 蛇河之後再翻越山嶺就可接上密蘇里河、密西西比河 走上北美洲的大平原。The Snake River and Missouri River connect to Yellowstone and get within ~10 miles of each other near the continental divide
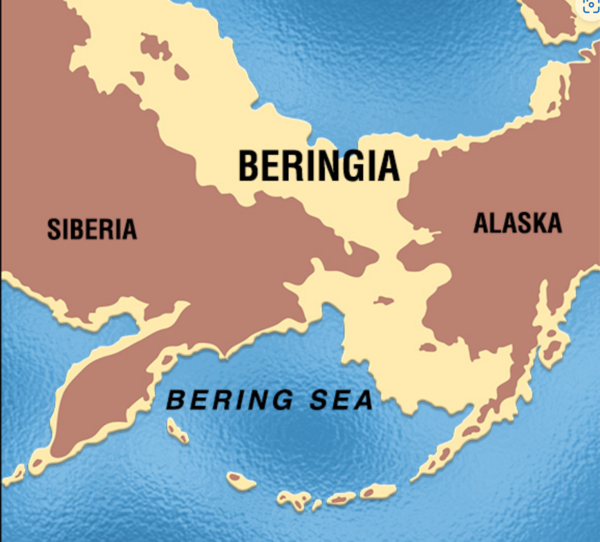
Twenty-five thousand years ago, during what is known as the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) of the Pleistocene Ice Age, glaciers up to two miles thick covered large parts of North America, Europe, and Asia and much of the earths water was locked up in the glaciers. Sea level at that time was significantly lower - up to 300 feet - and some areas that are now under water were dry land. The result was a land bridge connecting the continents of Asia and North America in the present day Bering Strait area and extending into the Bering and Chukchi seas. The land bridge was not a narrow isthmus(地峽), but rather a huge tundra(凍原) landscape, bounded by the stocky shoulders of two continents and stretching more than one thousand miles from north to south. As the climate began warming at around 18,000 years ago, the Beringia region also became more moist and the sea level rose, submerging the land bridge and causing the shrub tundra vegetation to expand. The first flooding of the land bridge happened around 10,000 years ago. 2009年在新墨西哥州(New Mexico)白沙國家公園(White Sands National Park)一個早已乾涸湖泊的湖底發現一批可追溯至約2萬年前的腳印化石,最近分析卡在腳印中種子,判定其年代約介於2萬2800年至2萬1130年前。(.:如果繼續沿海往南,就只有到了洛杉磯一帶可以上岸往東走,不必翻山越嶺(Santa Cruz Mountains,Sierra Nevada)。) 如果獅子是動物的森林之王,則人類是動物的地球之王,人類是地球上的頂級獵食者(hunter、predator)。而動物的生存法則就是要吃飽、還有不要被吃掉。動物求安全的方法就是往少危險、食物充足的地方移動,而獵人就追隨牠們往有很多獵物的地方移動,而人類對其他人類而言,就是獵場的競爭,趨於下風的獵戶或過多之組員就必須開拓新的獵場,這些因素促成了人類的全球擴張,人類分布到整個地球絕大部分的地方。其他動物都不是人類的對手,人類的擴張只受到大自然環境的考驗:極度寒冷、高山峻嶺、大河大海、沙漠荒野。 從人種可看出在最北方的是高加索人,皮膚比較白、頭髮瞳孔顏色比較淡,很明顯是北方的人種。而在東方的東亞人,皮膚是褐色、頭髮瞳孔顏色是黑色,很明顯是南方的人種。高加索人種往東走,東亞人種往北走,高加索人種在阿爾泰山、蒙古高原、黃河一線與東亞人種相逢,互相競爭,並且混種,出現了突厥人。 可說這兩種人種都去了美洲,可看出美洲的印地安人有兩種臉型。高加索人種很適應北美洲北方的氣候,所以就留在北美,而東亞人種則沿海邊就一直往南走,往溫暖的地區移動。所以,中南美的印地安人都是東亞人種的臉孔。
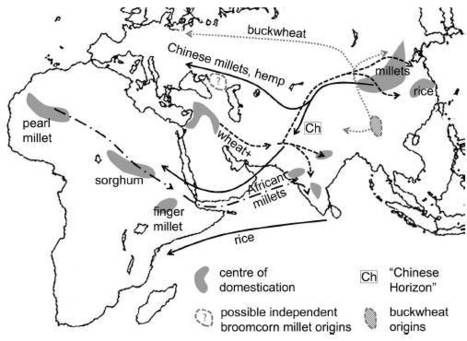
歐亞大草原 之後,農業興起,農業群體的人口快速增加,族群開始擴散。人類開始務農之後,食物有了保障,生活穩定了起來,新生兒的存活機率大增,人口就穩定成長,而有土就有生活保障,農業人口開始擴張找新地來耕種,也給不斷增加的人口有新的出路,農業群體以人數的優勢驅逐可耕地的原狩獵採集人,農業群體開始在全球擴張。 在歐亞大陸上,北方有歐亞大草原橫跨歐洲和亞洲,在歐亞大草原的下緣,在遠古有一條平行的農業區,當時氣候並沒有如現今的乾旱,農業群體就一直往東發展,接觸到東方的農業群體,形成一條橫跨東西的文化帶。之後,由於氣候變遷還有喜馬拉雅山不斷隆起,氣候開始變得乾燥,在此生死存亡之刻,緊急尋找更耐旱的作物,那就是中國西北耐旱的粟、黍(millet[ˋmilit]),但這條農業帶無法再持續,遠離海洋的地區開始無法耕種,人們由耕種、養殖轉為畜牧、放牧,再進一步形成游牧。游牧族群開始壯大,草原也開始定型。東西兩端間的農業文化開始消失,東西農業族群開始獨立發展。
Food globalization in prehistory, World Archaeology, 2011, 43(4), 665–75。a prehistoric ‘Trans-Eurasian’ episode of food globalization characterized by the long-distance exchange of starch crops.
古埃及文化的传播路线和区域 by Grafton Elliot Smith 有悠久歷史發展的埃及文明是沿著海路開始傳播古埃及文化,可以說中國在遠古是充滿了西亞文化,西亞文化由海路以及歐亞大草原傳到中國。
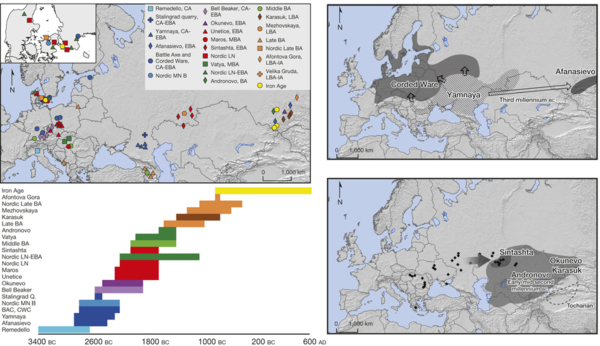
Population genomics of Bronze Age Eurasia
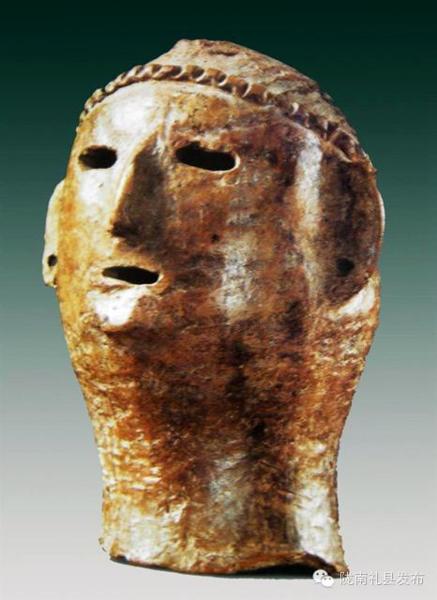
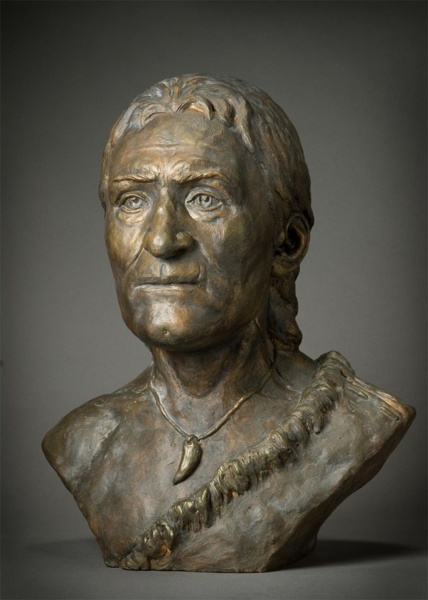
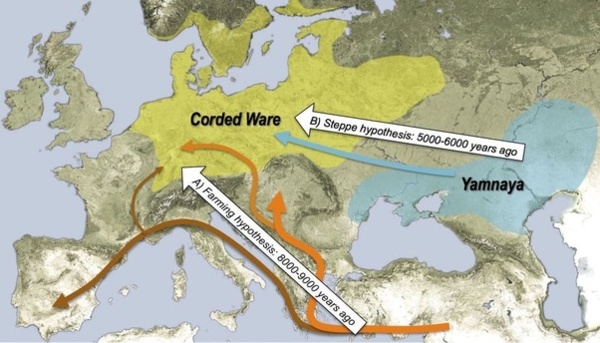
少女头像 1964年甘肃省陇南市礼县高寺头村出土,属仰韶文化遗物。残高12.5厘米,宽8.5厘米,陶色橙黄 接著,游牧群體開始興起,馬匹時代開啟,再加上已進入青銅時代,遊牧民族開始武力擴張,與農業群體開始長期鬥爭,首先是印歐人縱橫歐亞大陸,接著就是匈奴、突厥在歐亞大草原與中亞奔騰,接著就是蒙古人的橫掃千秋,中歐兩個農耕文明被遊牧族群割斷聯繫,直到槍砲時代的到來,遊牧族群的體能、機動優勢不再,俄羅斯控制了歐亞大草原與中亞,西方的船堅炮利來到了中國。 我說:人類的群體歷史就是平衡僵持、突破擴張的循環歷史。 ***************************** 17/5/26 罗马尼亚文化中心邀请两位罗马尼亚考古学家访华,与中国社会科学院考古研究所和中国社会科学院外国考古研究中心联合举办库库特尼-特里波利文化(c.5200 to 3500 BC) 和仰韶文化彩陶展及学术研讨会, 约公元前5000至公元前3000之间,辽阔的欧亚大陆东、西两端,两支灿烂的农业文化蓬勃发展。东面是以黄河中上游为中心的仰韶文化,西面是以黑海西部和西北部为中心的库库特尼-特里波利文化。她们都以发达的农业为基础,经济和社会组织高速发展,出现面积达100万平方米以上的大型聚落、大型公共建筑和绚丽的彩陶。尤为引人注目的是,两个相隔万里的文化的彩陶纹样有很多相似性。 库库特尼-特里波利和仰韶文化的相似性是学界热切关注的问题。关注的焦点有两个:其一,在丝绸之路开通数千年之前,是否已经存在跨越欧亚的“彩陶之路”,成为东西方之间交流生产技术和意识形态的重要通道;其二,分别孕育出这两支考古学文化的黑海地区和黄河中上游地区为何后来走上了截然不同的发展道路。 库库特尼-特里波利文化是罗马尼亚铜石并用时代重要的考古学文化,目前在罗马尼亚境内发现该文化遗址约2500处,乌克兰境内发现约2000处,其文化分布面积达35万平方公里,东部遗址出土彩陶比例超过百分之七十五,且制作工艺高超。从建筑上来看,多为木骨泥墙,房内常设火塘、磨石、窖穴等用于生产或贮藏用途。 遗址中出土有大量石器工具、红铜器以及与附近地区交换所得的燧石等石料。出土的典型器物为彩陶,一般以白、红、黑等颜色绘出几何纹,烧成温度约在950-1000摄氏度,遗憾的是库库特尼-特里波利文化尚未发现大型墓地。 陕西历史博物馆副馆长王炜林研究员首先阐述了庙底沟彩陶的扩张进程:先向东到达黄河中下游及淮河流域,再向西到达黄河上游地区,再到塞外的内蒙古中南部,又向南发展到长江中游地区,在这些区域都可以看到庙底沟文化彩陶的影子。 两地的彩陶文化衰落后,都发生了人群的迁移和社会动荡整合,但黑海沿岸地区在罗马帝国之前没有形成高级政体,而在中国,动荡整合的结果是陶寺和二里头这样的早期国家的出现。 中国西北地区的家羊、家黄牛、小麦、尖顶冠形符号、舞蹈纹、陶偶等先后西传而来,而中国彩陶文化也渐次分南道、北道西行,影响到费尔干纳盆地和克什米尔地区。 北京大学李水城教授认为中国西北地区的彩陶文化和早期中西交流彩陶的出现除了技术支持外还要受到社会、经济和环境等诸多因素的制约。无论中外,彩陶发达的地方都是黄土地带,这或许与黄土更适宜制作精致的浅色陶器有关。此外,黄土土质适宜发展旱地农业,因此早期彩陶往往与旱地农业和定居生活相关联,凡彩陶流行之地往往是农耕社会较早出现的地区。如近东的安那托利亚、两河流域、黎凡特等地。而中国最早的彩陶出现在西北渭河流域,此地也是最早种植粟、黍、大麻等旱地农作物的地区,驯养猪、狗等家畜。“彩陶生产极大推动了手工业的专业化和社会分工,由此加速了社会复杂化进程。”他还提出,彩陶发达的地区往往伴随丰富的卤水资源,可能与产盐相关。随后,李水城教授将特里波列-库库特尼文化Cucuteni-Tripolye、萨马拉文化Samara、哈拉帕文化Harappa、米哈伊洛夫卡Mikhailovka文化和仰韶文化、马家窑文化的陶器进行对比分析,他表示同一时代的同一风格是由背后的社会环境所造成的,“表面相似的真正原因其实是内在资源和环境相似”他说。 (.18/10/23:不是的,根本就是C-T人。那些陶器上的驚人圖案是獨立發展的機率很低,連體陶器更是不大可能。這個問題的迷濛處是東歐已不是西亞人種,而且C-T人應該是採火葬,找不到墳墓,而且馬家窯文化也是火葬。而中原地區由於混種程度很高也不見原來面貌。兩邊都有了徹頭徹尾的變化。) (注:據 《墨子·節葬下》記載:「秦之西有儀渠之國者,其親戚死,聚柴薪而焚之。」儀渠在今甘肅慶陽縣西南,這說明先秦時代的儀渠人是實行火葬的。历史记载表明羌人有三大特征:牧羊、火葬与羌笛。) 18/7/31 甘肃 经过8年的发掘,甘肃河西走廊早期冶金遗址考古工作有了重要收获。河西走廊的冶金活动在距今约4100-4000年的马厂文化晚期就已存在,至距今4000-3700年左右的西城驿文化时期,冶炼活动规模空前。西城驿文化和齐家文化在冶金遗址多有共存,形成“西城驿—齐家冶金共同体。 从2010年起,甘肃省文物考古研究所与中国社会科学院考古研究所、北京科技大学等联合对张掖西城驿遗址进行了8年的发掘。调查最后确定张掖西城驿,民乐东灰山、西灰山,玉门砂锅梁、古董滩,金塔火石梁、缸缸洼、白山堂铜矿等多处遗址与早期铜冶金活动相关。 西城驿遗址的发掘发现,铜冶金是西城驿遗址最具代表性的手工业,也是河西走廊新石器时代晚期至青铜时代最具特色的文化现象。西城驿遗址铜冶炼所用矿石主要来自河西走廊的北山地区。矿料分为两种,一种为仅含铜的氧化矿石,有些残留一定的硫化矿物;一种为含砷、铅、锑等合金元素的矿石。当时使用了“氧化矿—铜”的冶炼工艺,以冶炼红铜为主,存在先冶炼纯铜,在冶炼流程后段添加含砷、锡等合金元素的矿石炼制青铜合金的技术。 在河西走廊地区早期冶金发展中,马家窑—马厂—西城驿—四坝人群是冶金技术的主要掌握者,齐家文化正是通过与这支人群的交流,获取并广泛传播了冶金产品或冶金技术,从而对中国其他区域早期冶金技术产生不同程度的影响。 18/10/4 In 2014, an exceptional discovery made in Romania - a pre-cucuteni house with an age of about 7200 years -bring to light evidence of trade between residents in Romania and those from China ... The Cambridge team is to determine how 6-7000 years ago were made grain exchanges between Europe and Asia, but especially between Europe and China. In this context, we wonder whether the Neolithic cultures developed in an area encompassing Romania today, created influences far into Asia, the Carpathian-Danubian-Pontic space is not only home of old Europe, but as some foreign researchers say, is also a place from, where populations started to Asia that underpin the cultures of this continent ... 18/10/19 [Biology Letters] Dogs accompanied humans during the Neolithic expansion into Europe Dogs were the only domestic species present in both Europe and the Near East prior to the Neolithic. Here, we assessed whether early Near Eastern dogs possessed a unique mitochondrial lineage that differentiated them from Mesolithic European populations. Our results show that European pre-Neolithic dogs all possessed the mitochondrial haplogroup C, and that the Neolithic and Post-Neolithic dogs associated with farmers from Southeastern Europe mainly possessed haplogroup D. Thus, the appearance of haplogroup D most probably resulted from the dissemination of dogs from the Near East into Europe. . In Western and Northern Europe, the turnover is incomplete and haplogroup C persists well into the Chalcolithic at least. These results suggest that dogs were an integral component of the Neolithic farming package and a mitochondrial lineage associated with the Near East was introduced into Europe alongside pigs, cows, sheep and goats. It got diluted into the native dog population when reaching the Western and Northern margins of Europe. In Western Eurasia, settled agriculture and stock keeping first arose in the Fertile Crescent. This Neolithic way of life then emerged in Europe between 9000 and 6000 BP, triggered by the arrival of immigrant farmers approximately 9000 BP who originated in the Near East and substantially replaced the local hunter–gatherer population except on the Western and northern margin of the continent, where Mesolithic societies persisted longer. These farmers were accompanied by several domesticates including sheep and goats [6], pigs, cows and cultigens including wheat, barley, peas, broad beans and lentils. 18/10/19 [Biology Letters。June 21, 2016 ] Early farmers from across Europe directly descended from Neolithic Aegeans Farming and sedentism(定居) first appeared in southwestern Asia during the early Holocene and later spread to neighboring regions, including Europe, along multiple dispersal routes. Our study demonstrates a direct genetic link between Mediterranean and Central European early farmers and those of Greece and Anatolia, extending the European Neolithic migratory chain all the way back to southwestern Asia. It is well established that farming was introduced to Europe from Anatolia. Recent radiocarbon dating indicates that by 6600–6500 calibrated (cal) BCE sedentary farming communities were established in northwestern Anatolia at sites such as Barcın, Menteşe, and Aktopraklık C and in coastal western Anatolia at sites such as Çukuriçi and Ulucak, but did not expand north or west of the Aegean for another several hundred years. All these sites show material culture affinities with the central and southwestern Anatolian Neolithic. The high levels of shared drift between Aegean and all available Early Neolithic genomes in Europe, together with the inferred unique drift between Neolithic Aegeans and Early Neolithic genomes from Northern Spain to the exclusion of Early Neolithic genomes from central Europe, indicate that Aegean Neolithic populations can be considered the root for all early European farmers and that at least two independent colonization routes were followed. 18/10/19 [Nature。11 June 2015] Massive migration from the steppe was a source for Indo-European languages in Europe We generated genome-wide data from 69 Europeans who lived between 8000–3000 years ago by enriching ancient DNA libraries for a target set of almost 400,000 polymorphisms. We show that the populations of Western and Far Eastern Europe followed opposite trajectories between 8000–5000 years ago. At the beginning of the Neolithic period in Europe, ∼8000–7000 years ago, closely related groups of early farmers appeared in Germany, Hungary and Spain, different from indigenous hunter-gatherers, whereas Russia was inhabited by a distinctive population of hunter-gatherers with high affinity to a ∼24,000-year-old Siberian. By ∼6000–5000 years ago, farmers throughout much of Europe had more hunter-gatherer ancestry than their predecessors, but in Russia, the Yamnaya steppe herders of this time were descended not only from the preceding eastern European hunter-gatherers, but also from a population of Near Eastern ancestry. Western and Eastern Europe came into contact ∼4500 years ago, as the Late Neolithic Corded Ware people from Germany traced ∼75% of their ancestry to the Yamnaya, documenting a massive migration into the heartland of Europe from its eastern periphery. This steppe ancestry persisted in all sampled central Europeans until at least ∼3000 years ago, and is ubiquitous in present-day Europeans. These results provide support for a steppe origin9 of at least some of the Indo-European languages of Europe. 18/10/19 [Yofred Gonzalez。Oct 4, 2018] The most popular hypothesis on the origins of the first Indo-Europeans is the Kurgan hypothesis, which places the Proto-Indo-European homeland in what is now the Caucasus region and Russia, being the Yamnaya(Yamna) culture the oldest Indo-European culture at around 3300 B.C How did the Yamnaya look like? Did they look “mongoloid” aka like Chinese or Mongolian people? or did they look “Caucasoid” aka like modern Europeans. What about their skin, hair and eye color? Well, let´s look at the evidence. This is a reconstruction of a Yamnaya person based on cranial research. As you can see here, he looks quite Caucasoid.
What was the skin and hair color of Yamnaya people? Yamnaya people were predominantly a dark haired and brown-eyed people with light skin. They lacked the Melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) responsible for blond, red and light-colored hair and the oculocutaneous albinism II gene responsible for light eyes but they carried the SLC24A5 and SLC45A2 genes responsible for light skin.
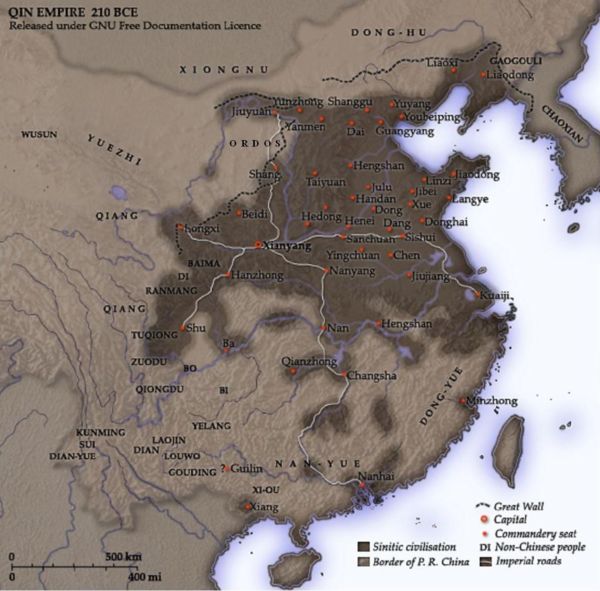
The second oldest Indo-European culture is the Corded Ware culture (3.000 B.C to 2.600 BC), the one that gave origin to Celtic, Slavic, Baltic and Germanic languages. How did these other people look like? Well, in contrast with the Yamnaya. All the genes that i mentioned responsible for light hair and eyes that were lacking among the Yamnaya were pretty common among the Corded Ware people. Why? Because the Corded Ware people were a mixture between Yamnaya I.E and the Neolithic people of Northern and Eastern Europe that carried these light features. Its because of this fact that the genes responsible for light features are common among the people of the Andronovo Culture founded by Corded Ware settlers in Central Asia. Andronovo people are associated with the earliest Indo-Iranian languages that later spread to West Asia. (.:中原也發生了 繩紋陶代替了彩陶。) 18/10/19 The people of the Yamnaya culture were the likely result of admixture between Ancient North Eurasians (via whom they also descend from the Malta–Buret culture or other, closely related people such as Siberians and Native Americans) and an early caucasian Near Eastern people related to Early Neolithic Farmers. Their material culture is very similar to the Afanasevo culture, their contemporaries in the Altai Mountains; furthermore, genetic tests have confirmed that the two groups are genetically indistinguishable. The Yamna culture originated in the Don–Volga area, and is dated 3300–2600 BC. It was preceded by the middle Volga-based Khvalynsk culture and the Don-based Repin culture (ca. 3950–3300 BC), and late pottery from these two cultures can barely be distinguished from early Yamna pottery. 18/10/19 More than 5000 years ago a nomadic group of shepherds rode out of the steppes of eastern Europe to conquer the rest of the continent. The group, today known as the Yamna or Pit Grave culture, brought with them an innovative new technology, wheeled carts, which enabled them to quickly occupy new lands. More than 4,500 years ago, the descendants of these people reached the Iberian peninsula and wiped out the local men. The Iberian peninsula was not only colonized by the first Neolithic migration wave 8,000 or 9,000 years ago but also by a later one 4,500 years ago, which brought with it a very different culture. War axes and carts with four wheels can be found in the layers of earth that date back 4,500 years. From then on, almost all men’s tombs were filled with weaponry, adornments, displays of wealth. The archaeology reveals marked signs of a hierarchical society that broke with the old egalitarianism of the early Neolithic period. In terms of why the Y chromosome was replaced, the populations from the steppes had superior technology, better weapons and also domesticated horses that could have given them an advantage in war. 18/10/19 The Ordos(鄂爾多斯) culture was a culture occupying a region centered on the Ordos Loop(河套文化) (modern Inner Mongolia, China) during the Bronze and early Iron Age from the 6th to 2nd centuries BCE. The Ordos culture is known for significant finds of Scythian art and is thought to represent the easternmost extension of Indo-European Eurasian nomads, such as the Saka. Under the Qin(秦) and Han dynasties, from the 6th to 2nd centuries BCE, the area came under at least nominal control of contemporaneous Chinese states.
這張秦朝地圖與教科書上繪製的有些不同 The Ordos Plateau was covered by grass, bushes, and trees and was sufficiently watered by numerous rivers and streams to produce rich grazing lands. At the time, it contained the best pasture lands on the Asian Steppe. However, it has now mostly turned to the Ordos Desert through a combination of overgrazing and climatic change.
As the Xiongnu expanded southward into Yuezhi(月氏) territory around 160 BCE under Modun, the Yuezhi in turn defeated the Sakas and pushed them away at Issyk Kul. It is thought the Xiongnu also occupied the Ordos area during the same period, when they came in direct contact with the Chinese. (注:義渠,又稱儀渠、戎,古代部族國家,活躍於今涇水北部至河套地區,最初以遊牧為生。在殷商末年形成國家,逐步定居。至戰國時代,佔有今天的陝西省北部、甘肅省北部和寧夏等地,與秦國形成對抗關係,最後被秦國所滅。傳統上將他們列為西戎之一。義渠最重要的民俗特徵是火葬。) (.:上面說法不大一致,可能是為匈奴所滅。周人從未有人說戎人長相特異,可見周人就是戎人(或C-T人),長相是一樣的。而商人應該是東亞夷人。) 18/10/20 Neolithization of the Steppes occurred by incoming farmers from Iran - South Central Asia (Eastern parts of the Iranian Plateau) and not from Anatolia or Levant... Neolithization of Southern and Central Europe occurred by incoming farmers from Anatolia. [http://hms.harvard.edu/news/meet-first-farmers] [http://www.sciencemag.org/news/2016/...singly-diverse] 18/10/20 The Cucuteni–Trypillia culture flourished in the territory of what is now Moldova, northeastern Romania and parts of Western, Central and Southern Ukraine. During the Atlantic and Subboreal climatic periods in which the culture flourished, Europe was at its warmest and moistest since the end of the last Ice Age, creating favorable conditions for agriculture in this region. • Early (Pre-Cucuteni I–III to Cucuteni A–B, Trypillia A to Trypillia BI–II): 4800 to 4000 BC (注:In Ukraine, the Trypillian culture (TC) existed for over two millennia (ca. 5400–2700 BCE) ) (.:5400與4800差了600年,哪一個是對的?) Early period (4800–4000 BC) Late period (3500–3000 BC) According to some proponents of the Kurgan hypothesis of the origin of Proto-Indo-Europeans, the Cucuteni–Trypillia culture was destroyed by force. These proponents of the Kurgan hypothesis hold that this invasion took place during the third wave of Kurgan expansion between 3000–2800 BC, permanently ending the Cucuteni–Trypillia culture. There is the limited common historical life-time between the Cucuteni–Trypillia (4800–3000 BC) and the Yamna culture (3300–2600 BC); given that the earliest archaeological findings of the Yamna culture are located in the Volga–Don basin, not in the Dniester and Dnieper area where the cultures came in touch, while the Yamna culture came to its full extension in the Pontic steppe at the earliest around 3000 BC, the time the Cucuteni–Trypillia culture ended. The transition to todays arid climate was not gradual, but occurred in two specific episodes. The first, which was less severe, occurred between 6,700 and 5,500 years ago. The second, which was brutal, lasted from 4,000 to 3,600 years ago. Summer temperatures increased sharply, and precipitation decreased, according to carbon-14 dating. According to that theory, the neighboring Yamna culture people were pastoralists, and were able to maintain their survival much more effectively in drought conditions. Toward the end of the Cucuteni–Trypillia cultures existence (from roughly 3000 BC to 2750 BC), copper traded from other societies (notably, from the Balkans) began to appear throughout the region, and members of the Cucuteni–Trypillia culture began to acquire skills necessary to use it to create various items. Along with the raw copper ore, finished copper tools, hunting weapons and other artefacts were also brought in from other cultures. This marked the transition from the Neolithic to the Eneolithic, also known as the Chalcolithic or Copper Age. Bronze artifacts began to show up in archaeological sites toward the very end of the culture. The primitive trade network of this society, that had been slowly growing more complex, was supplanted by the more complex trade network of the Proto-Indo-European culture that eventually replaced the Cucuteni–Trypillia culture. Cucuteni–Trypillia tools were made from knapped and polished stone, organic materials (bone, antler and horn), and in the later period, copper. Weapons are rare but not unknown, implying the culture was relatively peaceful. The mainstream academic theory is that writing first appeared during the Sumerian civilisation in southern Mesopotamia, around 3300–3200 BC. in the form of the Cuneiform script. This first writing system did not suddenly appear out of nowhere,[original research?] but gradually developed from less stylised pictographic systems that used ideographic and mnemonic symbols that contained meaning, but did not have the linguistic flexibility of the natural language writing system that the Sumerians first conceived. These earlier symbolic systems have been labelled as proto-writing, examples of which have been discovered in a variety of places around the world, some dating back to the 7th millennium BC. Beginning in 1875 up to the present, archaeologists have found more than a thousand Neolithic era clay artefacts that have examples of symbols similar to the Vinča script scattered widely throughout south-eastern Europe, and was used throughout the geographical region of the Cucuteni–Trypillia culture. There was no occupational specialization, or division of labor as economists call it. When people specialize in their best skills, they become more expert at them, which increases the societys productivity and elevates its level. They also, of necessity, have to exchange goods and services with each other, which is the beginning of a civilized economy. There was no social stratification. No rulers, no police, no priests, no teachers, no merchants, no elite. This is a requirement for a city with division of labor, in which procedures must be developed to aid the citizens in living in harmony, fairness and cooperation with strangers. The T-C people had a subsistence economy, or at best a gift economy, which relies on altruism among strangers rather than fair exchanges. 18/10/20 The major impediment in the study of the genetic origins of the carriers of TC is that while leaving behind great volumes of material culture evidence, very little trace of TC inhabitants themselves remains. In fact, human burials are virtually unknown until the final part of TC chronology . The only TC site discovered to date that contains a continuous record of human osteological deposits is a gypsum cave called Verteba located in the Podillya region of western Ukraine. (.:找不到墳墓,聯想到C-T人會幾代後燒掉住區重建,可見C-T人非常害怕瘟疫,所以,很可能死人是都燒掉了。) The mtDNA haplogroup diversity found in the TC remains at Verteba is, overall, typical of a group of European Neolithic farmers tracing their maternal genetic roots from Anatolia with little or no admixture with indigenous hunter-gatherers. 18/10/20 仰韶文化是黄河中游地区一种重要的新石器时代彩陶文化,仰韶文化绝对年代在4933BC~2923BC左右,其延续时间约2000年。其分布范围,东起豫东,西至甘肃、青海,北到河套内蒙古长城一线,南抵江汉,中心地区在豫西、晋南、陕东一带。 陶器以细泥红陶和夹砂红褐陶为主,主要呈红色,多用手制法,用泥条盘成器形,然后将器壁拍平制造。红陶器上常有彩绘的几何形图案或动物形花纹,是仰韶文化的最明显特征,故也称彩陶文化。 仰韶文化是一个以农业为主的文化,以种植粟类作物为主。其村落或大或小,比较大的村落的房屋有一定的布局,周围有一条围沟,村落外有墓地和窑场。村落内的房屋主要有圆形或方形两种,早期的房屋以圆形单间为多,后期以方形多间为多。房屋是泥草混合形式,房屋的墙壁是泥做的,有用草混在里面的,也有用木头做骨架的。墙的外部多被裹草后点燃烧过,来加强其坚固度和耐水性。仰韶文化和龍山文化(3000-2000B.C )都是屬於半地穴居。 仰韶文化的分期大致可分为早、中、晚三期,早期分三段,5000BC ~4900BC ~4300BC~4000BC。中期(4000BC~3500BC)。晚期典型(3500BC~2900BC)。 18/10/20 大地湾位于天水市渭河上游的秦安县五营乡邵店村东侧。 大地湾一期文化的绝对年代为公元前6220--前5360年,其问跨度约900年,这是迄今所知在甘青地区新石器时代早期文化同类遗址中年代最早的。大地湾1期文化早于中原仰韶文化的典型代表半坡文化千年以上,两者在文化原貌上又有延袭承传的密切关系。 大地湾遗址、师赵村遗址发掘房屋遗址200多座,最早的是深穴窝棚式建筑,这是标志着人类的居住方式从穴居向半穴居迈进的一个新起点。这时的人们已经开始有意识地处理死者,他们挖掘长方形竖穴土坑作为墓室,葬式有仰身直肢葬、屈肢葬和瓮棺葬等多种形式。 在大地湾一期灰坑中,采集到已碳化的禾本科的黍和十字花科的油菜籽,其中黍的碳测年代距今约7000多年,是中国同类作物中时代最早的标本。说明陇原大地最早的垦荒者至少在7000多年以前就成功地将野生黍培养成裁培黍,确立了中国黍源于陇西黄土高原的说法,证明了以大地湾遗址为中心的清水河谷是中国最早的粮食和油料作物的种植地,也是中国旱作农业黍、稷的发祥地。 大地湾一期文化主要分布在渭河中上游地区,在泾水、西汉水上游以及丹江上游也发现少数遗址。除甘肃省内有重要遗址外,在陕西省境内也有不少遗址。大地湾一期文化遗址有其独具的特征,包括以下几个方面的内容: 18/10/20 “全国十大考古新发现”评选自1990年启动以来,四川考古成绩卓著,迄今已有12项入选“十大发现” 成都平原史前古城址群是指分布于成都市的新津宝墩遗址、温江鱼凫村遗址、郫都区古城遗址、都江堰芒城、崇州双河以及紫竹等6处古城,面积11万至60 万平方米不等。古城群属宝墩文化,是三星堆文明的前身,是迄今所知我国西南地区发现的年代最早、规模最大、分布最密集的史前城址群。 刘家寨遗址是四川发现的一处新石器时代晚期遗址,距今大约5000年,位于阿坝州金川县二嘎里乡二级阶地刘家寨。有专家认为,这或许是一个以陶制业为主的聚落。在这里出土的带柄石斧、鹤嘴石锄等利用天然形状略作加工的大型石器,是四川的首次发现。这处面积仅有3500平方米的史前遗址,虽然不大,却是首次在川西北大渡河上游的大小金川一线发现距今5000年前后的马家窑文化,被认为填补了大渡河上游新石器考古的空白。 金沙遗址,于2001年2月开始进场组织发掘,分布面积在3平方公里以上,是一处大型的商周时期蜀文化中心遗址,极有可能是三星堆文明衰亡后在成都地区兴起的一个政治、经济、文化中心,或为古蜀国的又一都邑所在。出土的太阳神鸟金箔被确定为中国文化遗产标志和成都城市形象标识主图案。 金沙遗址可能是三星堆文化的直接继承地。金沙遗址已经出土了大量类似三星堆文化的器物。 目前三星堆和金沙都没有发现实用兵器。金沙发现的一些玉器与陕西石峁遗址(新石器晚期到夏早期)出土的玉器很相似。而类似中原地区二里头文化、商文化的文物,在金沙也有发现。类似三星堆、金沙的文物在越南也有发现。如果将三星堆、金沙出土的玉璋和越南出土的玉璋放在一起,一般人是分不清的。还有凹刃玉凿,这个器物在三星堆、金沙有出土,此外就是越南和中越边界出土过,其他地方都没有。我们认为古代蜀国和东南亚的交流是十分频繁的。 金沙遗址主要研究重点在玉器上。因为金沙出土的玉器非常多,种类也非常多,而且色彩非常丰富,在全国范围内是独树一帜的。金器也是一个重要的研究方向,因为三星堆、金沙出土的金器很多,和其他地方出土的金器功用很不同。 在发掘三星堆遗址青关山土台的过程中,在南侧大型建筑群和北侧青关山城墙之间的凹地中发现了一个灰坑,出土了大量完整的或可复原的陶器。该遗址还出土了玉器、金箔、绿松石、兽牙和铜渣等,都和陶器是同时期的文物。由此可证实,三星堆城址在此时并未废弃,甚至还有城墙补筑的现场。这些发现意味着,三星堆城址作为古蜀国都城的年代可能要往后推移大概50年左右,也就是公元前1150年左右。三星堆遗址和金沙遗址作为古蜀国都城,是前后相接的,因此,金沙遗址作为都城的年代也将往后推移,即商代晚期偏晚阶段。 17/10/22 巴拿马有1/10人带有中国血脉,依然使用中国姓氏 今天巴拿马的华侨华裔大多出自清末来到美洲的华工,勤俭的华工更容易积蓄财富,但政治上没有地位,便经常成为迫害的对象。曾经有一段时间,巴拿马甚至立法剥夺华侨的财产。 为了避免血汗积蓄被掠夺,那时在巴拿马的华工不得不尽量寻找其他种族女子通婚,以便将财产转移到妻子或子女的名下。这使巴拿马的华裔面孔与祖先发生了极大的变化,只有他们的姓氏,承载着对母国的眷恋和对故乡的相思。 (.:只有150年期間,面貌就變得看不大出來了。) 18/10/23 前苏联学者瓦西里耶夫曾在其专著《中国文明的起源问题》中,他认为把两河流域哈苏纳文化萨玛拉时期的彩陶,同马家窑文化半山类型彩陶的塑像做对比,就会发现二者的共性是无疑的,半山塑像应是美索不达米亚样品的‘中国变体’。再比如锯齿纹,是马家窑文化彩陶上的一种具有代表性的纹饰。锯齿纹基本只存在于半山类型上,其他类型山极少出现。锯齿纹实际上是古羌人对山崇拜的纹饰他演变。在中国之外,从西亚、北非、欧美等地区出土的器物(包括彩陶)来看,锯齿纹应该是具有世界性的一种文化现象。另外,马家窑文化上出现的“卍”符号,在欧洲希腊等地、非洲古埃及、美洲印第安等地区都广为流传。对于这种造型上的近似性和纹饰上的相近性,我们不能简单的用偶合来解释,他实际上反映了一种文化的交流和传播。 马家窑人是不是可以认为也属于古羌人呢?答案应该是肯定的,因为我们可以从马家窑文化及其承续文化(齐家文化、辛店文化、寺洼文化、卡约文化、沙井文化等)中找到“羌”的元素。 早在1940年代,夏鼐就在《临洮寺洼山发掘记》一文中指出寺洼文化与羌文化有关,他主要是从寺洼文化的火葬葬俗方面来讨论的。1979年,张朋川先生在《甘肃出土的几件仰韶文化人像陶塑》一文中介绍了甘青地区出土的几件人像陶塑,他认为甘肃地区从庙底沟到马厂时期的陶塑人像都是披发的发式,而殷周秦汉时期活动在甘青地区的羌族发式也是披发的,因此可以认为他们之间存在民族属性的承继关系。后张广立、赵信、王仁湘三人在《黄河中上游地区出土的史前人形彩绘与陶塑初释》中进一步从披发、衣尾、火葬和白石崇拜几个方面来探查羌人的风俗,他们认为,早在新石器时代,古代以至现代羌人的一些独有风俗就开始逐渐形成了,而马家窑文化和齐家文化时期是古羌族系统的形成时期。而俞伟超更在《古代“西戎”和“羌”“胡”文化归属问题的探讨》和《关于“卡约文化”的新认识》两篇文章中认为,马家窑、半山、马厂类型和齐家文化是羌人文化的前驱,在湟水一带的唐汪、辛店文化是羌人的文化遗存,而卡约文化是以羌人为主体的西戎诸部落的文化遗存。按照他的意见,甘、青地区已知的诸彩陶文化类型都是古羌人文化遗存。 从伊朗以东至甘肃黄河流域,特别是黄河流域一级支流——洮河流域,再到渭河流域、汉水流域、岷江流域,直至长江金沙江流域,这些地方竟然也是马家窑文化的分布区和延伸承续文化区。既是一条长长的文化带,又是一条文化带上独具特色的文化节点。 (.:這樣說來,古羌人就是C-T人,西亞人。而戎人就是印歐人。) 18/10/24 The genetic history of Europe since the Upper Paleolithic is inseparable from that of wider Western Eurasia. By about 50,000 years ago (50 ka) a basal West Eurasian lineage had emerged (alongside a separate East Asian lineage) out of the undifferentiated "non-African" lineage of 70 ka.The basal Western Eurasians were early exposed to significant Neanderthal admixture. Introgression of Neanderthal traits persisted in European populations into the present, affecting traits such as skin tone and hair color, height, sleeping patterns and mood. 18/11/6 维吾尔族先民的主体是隋唐时期活动在蒙古高原的回纥人。当时,为了反抗突厥的压迫和奴役,回纥联合铁勒诸部中的仆固、同罗等部组成了回纥部落联盟。元明时期,新疆地区各民族进一步融合,蒙古人尤其是察合台汗国的蒙古人基本和畏兀儿人融为一体,为畏兀儿补充了新鲜血液。 据史料记载,突厥是6世纪中叶兴起于阿尔泰山地区的一个游牧部落,于552年消灭了柔然汗国,建立突厥汗国。维吾尔族先民回纥早期受突厥统治。为了反抗突厥压迫和奴役,回纥联合铁勒诸部中的仆固、同罗等部组成了回纥部落联盟,配合唐朝军队消灭了突厥汗国。突厥作为我国古代的一个游牧民族,也随着汗国的消亡于8世纪中后期解体,从此,突厥在我国北方退出历史舞台。历史上维吾尔族先民和突厥人虽然长期在同一地域生活,但并不是突厥人。 目前我国使用突厥语族语言的民族有维吾尔、哈萨克、柯尔克孜、乌孜别克、塔塔尔、裕固、撒拉等,这些民族都具有各自历史和文化特质,并不是所谓“突厥族”的组成部分。不能因为同操突厥语族语言,就把他们说成是突厥人。把维吾尔人说成是突厥人的后裔,这是完全违背历史事实的。同时也要看到,维吾尔人更与土耳其没有关系。 18/11/21 [.] 今天看到一張三星堆文物的圖片,可以佐證遠古中國大地充斥著西亞文化。
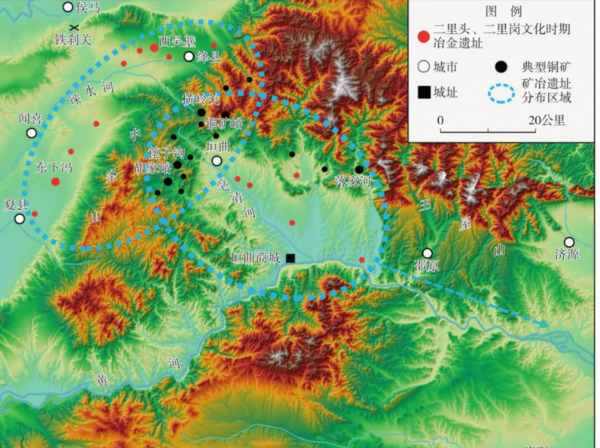
先看三個銅像的頭頂,中間的讓人想到猶太人頭上戴的小帽,兩邊的頭頂讓人想到東正教牧師戴的圓筒帽,還有土耳其人戴的圓筒帽。再來看他們的鼻子,很明顯這是西亞人的鼻形,比較突出的眼睛也是。有一點要注意到,猶太人是保存傳統最悠久的民族。 18/11/21 2011年歲末,在四川省德陽市羅江區城南的周家壩修路工地,考古人員發現了距今2300年前的開明王蜀時期的船棺墓葬群。如今,隨著發掘工作的全面展開,有望進一步揭開開明王蜀所封的孱侯國之謎。 (.:為什麼是船型?為什麼要吊在懸崖上?很簡單,就是發過大水,慘痛的經驗,現在就是要去查四川盆地歷史上有沒有發過大水,如果沒有,代表這是西亞文化,因為西亞很多紀錄(比如聖經),表明西亞人曾經經歷過大水。) 18/12/5 自19世纪中叶,美国探险家在中美洲的热带雨林中发现玛雅古遗迹以来,揭开了人类文明的另一种辉煌图景。玛雅文明诞生于公元前10世纪,约相当于中国的西周时期,公元4~9世纪进入繁盛期,继而从繁盛日益走向衰落。因其高超的文明成就,玛雅被称为“美洲的希腊”。玛雅人早在公元前4至3世纪就建立了二十进位算数系统,并发明了零的概念,直到1000多年以后,阿拉伯数字中才首次出现了数字“0”;玛雅人算出地球公转一年为365.2420天,比现代天文学测定的365.24219天领先一千多年,除此之外,他们还准确地推算出了月亮、金星的运行周期;卓尔金历是古代玛雅重要的历法之一,以20个神明图像代表天数,0到12的13个数字代表月,不断组合循环组成一年260天,竟与中国古代“天干地支”的组合方式类似;玛雅金字塔的修建更是集合了当时最先进的建筑技术和天文成就,台阶、朝向、角度均经过精密测算,标志节气、日出日落、星辰运行等自然规律。时至今日,这些成就仍与谜团并存。 18/12/29 [.] 山東人為何如此高大,可能的解釋就是C-T人早先是橫貫華北,但之後被來自東北的東亞人不斷往南衝擊,最後,C-T人據守山東的山嶺地形殘存了下來。 (注19/2/9:舉巨石強森為例,太平洋島國薩摩亞,統屬於玻里尼西亞人。這個人種據考古學家和人類學家研究發現,是當初從東亞沿著東南亞最後到太平洋的小島上的,和山東大漢們是同一個祖先。基因好,外加天平洋島國環境艱苦,練就了玻里尼西亞人的好身板,他們身材普遍高大,被稱為」世界上最強壯的民族。) (.:那之前的推論就是錯的?是走海路來的?) 19/2/8 1994年,一支來自法國的考古隊前來外蒙古的草原上對於古代匈奴的墓葬群進行挖掘,在布爾汗山的附近找到於96座從公元前1世紀便修建的古墓。經過DNA檢驗後發現,這些屍骨的DNA相當千奇百怪,不但有些與突厥人的基因,甚至還有些混有高加索人種的基因。 雖說匈奴人是否為同一民族目前尚未有定論,不過他們包含了蒙古語族、突厥語族、烏拉爾語族…等成員,可以顯現是由眾多部落與種族組成,但其最主要的統治民族應該為蒙古系統的部落。 19/2/20 在英国人宣称找到了“蓝眼睛、黑皮肤、黑卷发”的祖先后,瑞典电视台最新播出了一档系列纪录片《第一批瑞典人》(Meet The First Swedes),这部纪录片声称用DNA技术向人们详述瑞典人是如何在冰河时代之后生活的。大约在1.1万年前,拥有“黑皮肤、蓝眼睛”的第一批开拓者从南方进入了瑞典,最先生活在南边的省份斯科纳和西边的布胡斯,他们在不断的尝试中学会了利用海洋资源。随着气候变暖,他们开始向北迁徙并与来自寒冷的挪威北部的人口混合在一起,由于这里的紫外线辐射比较低,因此皮肤中的维生素D增多,肤色也变得越来越亮,直到变成了如今的白色。 2014年,西班牙巴塞罗那生物医药研究所的研究团队根据7000年前生活在西班牙一名狩猎采集者的DNA信息发现,古代欧洲人有黑色皮肤和蓝色眼睛。 据BBC报道,该团队还发现,早期欧洲人与瑞典和芬兰人的遗传关系最为密切。 2018年,研究人员通过提取DNA分析,生活在1万年前的英国人是拥有蓝眼睛的黑人。 19/3/3 由12位英國地質學家和考古學家組成的研究團隊,發現,組成英格蘭的「巨石陣」(Stonehenge)的石頭來自約240公里外、位於威爾斯西部的兩座採石場。研究團隊在採石場發現史前工具及挖掘石頭的遺跡。 巨石陣最早可追溯於公元前3000年左右,巨大石頭圍成環狀,從缺口往另一塊孤立的石頭「希爾」望去,剛好是夏至當天太陽升起的方位。 22/7/15 中科院昆明动物所专家对在云南蒙自发现的“马鹿洞人”头骨化石开展古DNA遗传学分析研究。结果发现,中国南方的古人类和最早的美洲土著人类之间存在深度的古老祖源遗传联系。这表明东亚人群在一万两千年前左右,确实可能从东亚大陆跨过白令海峡,最后迁徙到美洲,成为古印第安人的祖先。 22/11/23 Netflix《遠古啟示錄》(Ancient Apocalypse)記者葛瑞姆‧漢卡克(Graham Hancock) 遊遍全球,尋找遠至冰河時期各種神秘失落文明的證據。 (.:從這影集看到很多 巨石遺跡,很有意思。尤其是爪哇島 還有美國境內的遺跡。) (.:學術論文是要solid證據的,非常嚴謹的,這樣才能聚積智慧接力往前行。我們只能說考古學者無法為主角論述背書,但應該不會仇視或對抗他。史前文明因為沒有文字描述,就很難考,何況是史前失落的文明。不過,他的很多說法應該是正確的,星象是遠古人的重要觀察,地球的氣候變化是與地球的運動有關,而對地球的運動的觀察可透過對星象的觀察而得知,人類要在地球存活就要對氣候要有好的判斷,其中就是要知道春分與秋分,尤其是秋分,代表寒冬將至,在石器時代如何抓住秋分日,當然就是以石建築來標定最好,這就很好說明巨石陣的來由。當時應該是沒有文字的文明,所以應該是沒有數學的,很可能只是用到耐心的紀錄與歸納。沒有使用金屬能力(銅、鐵)的文明的極致可到什麼程度,可能比我們想像的要強。巨蛇的形象會不會是從天而降的彗星,有如一條大蛇。) (.:寫上一段的還未看第六集,果然,第六集提到 大蛇就是天降彗星。) (注:巨蛇丘 (The Great Serpent Mound) 位於俄亥俄州的南部,是美國東部眾多來歷不明的巨型人造土丘之一。這座土丘寬約6米,高約1.7米,整體長度為382.5米,蛇身總長更達600米左右。) (.:如果 巨蛇丘 是 代表 蛇張巨口 要吞 地球, 那麼 那個時期的人知道地球是圓的?) 22/12/4 八千年前,聪明的中國古人从通过影子测太阳到发明仪器测影以建立时空为主的天文知识。 23/11/15 可看到 影片中的地圖 黃河北邊 還有 一條河。 23/11/25內容很多,其中提到 中原缺錫這點很重要,這讓人想起 紅山文化。另外對比 美洲銅的使用,也間接證明,美洲原住民是早於中國銅器時代之前到達美洲,此外,也證明,縱然有豐富的銅礦,沒有技術經驗,也不知如何使用,或許也證明了中原銅冶煉是從西邊傳過來了。既然銅冶煉是西方傳過來的,當然,宗教、文字概念也會傳過來(發明甲骨文的人,應該是已經有文字使用的概念)。很有趣,人會逐獵物、沃土而移動,也會逐礦場而移動,美國不是發生過加州、阿拉斯加 掏金熱。 23/11/25 青銅是銅與錫的合金。在青銅生產中,錫料是不可或缺的資源。然而,時至今日,考古學家隻在中原地區發現有先秦銅礦開採遺址,卻尚未發現錫礦開採遺址。當時中原地區輸入燕遼地區鉛料、銅料的同時,也輸入了燕遼地區的錫料。該地區不但銅礦、鉛礦資源豐富,更不乏錫礦資源,例如黃崗梁—浩布高錫多金屬成礦帶目前所知是長江以北最大的錫礦帶。在大興安嶺南端赤峰一帶分布著大小200多處錫礦。在遼西找到了5處錫多金屬原生礦開採遺址。這些遺址的規模都比較大,有成百上千的採礦石器留在了當地,年代相當於中原的商代晚期。商王朝向南擴張,除了獲得銅,更主要的是為了獲得錫。因為中原本身就有銅,比如中條山。青銅器銘文‘金道錫行’,就指向南方。這些年,沒有在南方找到冶煉遺址,同時南方的採礦遺址很多也都被摧毀了。 23/11/25 錫是製造錫青銅的重要金屬,它的獲得是青銅時代以來古代文化的重要組成部分。公元前 3000 年左右,它開始在中東和巴爾幹地區使用。錫是地殼中相對稀有的元素,其豐度約為2 ppm,而鐵、銅、鉛、鉛、砷、銀和金的豐度分別為50,000 ppm、70 ppm、16 ppm、5 ppm、0.1 ppm 。 0.005ppm。因此,古代錫資源稀缺,通常必須進行很長距離的貿易才能滿足錫礦稀缺地區的需求。 錫的提取和使用可以追溯到公元前 3000 年左右的青銅時代初期,在銅中添加第二種金屬會增加銅的硬度,降低其熔化溫度,產生更具流動性的熔體,並將其冷卻成更緻密、海綿狀程度更低的金屬,從而使鑄造更容易。近東青銅技術的發展經歐亞草原傳遍中亞,帶來了錫勘探和開采的知識和技術。公元前2000年至1500年,烏茲別克斯坦、阿富汗、塔吉克斯坦開發了錫資源,並沿著絲綢之路穿越中亞向東西方輸送資源。該貿易聯繫基於青金石(一種珍貴的藍色半寶石)和來自中亞的綠松石裝飾綠泥石容器的現有貿易路線,這些容器最西遠達埃及,可追溯到同一時期。據認為,最早的錫是在公元前 2500 年至 1800 年的二里頭和殷朝沿黃河開采的。從漢代起,中國就從現在的雲南省進口錫。 23/11/25 [linyi812] 商代青铜器原料的来源是哪里? 中条山地区可能在龙山时期开始有铜冶炼,二里头(夏)-二里岗(早商)时期已经成熟并成规模,发现多处采矿和冶炼遗址
晋南地区夏及早商时期的城址、冶金遗址及矿山,二里头在右下角。這就說明 中華文明在這裡突起 的原因,器也,銅器讓其出類拔萃。良渚文化沒有銅器,是石器時代發展的最顛峰時期,是中華文化的濫觴 在二里岗上层偏晚阶段,中条山地区的矿冶活动逐渐陷入了停滞(到战国时期又重新开始)。这可能是由于表层铜矿开采殆尽而当时尚未完全掌握深层铜矿开采技术。恰在此时,长江中下游地区的矿冶活动兴盛起来,这应该是商王朝铜矿冶基地向南转移的结果。晚商时期的铜料主要不是来自中条山区。 ********************* 美 洲 ************************* 23/11/15 The Genetic Link Between Native Americans and the Chinese 23/11/15 The First Americans 24/1/16 Montana Megaliths 自從知道 一首雙身蛇後,怎麼看什麼都像 一首雙身蛇。如果真的是,就是祭拜祖先了。片中第一個應該是人為的(會不會是上面的石頭掉下來把下面的巨石撞裂,但是自然的石頭不會這麼方正。),其他不好說。有一可能就是這裡原來住了非常多的人,並在山上建了神殿,之後,那場驚人的雪壩崩塌,超大洪水讓無數的人喪生,這裡的文明消失了。 24/1/16 [.] 對非農耕人來說,平原可能不是最好的生活區,獵物多的地方才是,有山有水的地方是好的選擇。從亞洲東渡來美洲的人 在哥倫比亞河入海口溯河而上,轉入蛇河之後,再往東走,就會來到 Montana。
可看到 黃石公園 邊 就是 密蘇里河 Native Americans have lived along the Snake for more than 11,000 years. Salmon from the Pacific Ocean spawned by the millions in the river and were a vital resource for people living on the Snake downstream of Shoshone Falls. (.:所以這裡的人 河裡有 鮭魚,到處有野牛(Bison),生活沒問題。) 我的判斷,這不是水道,因為片中提到在山頭有四條不同方向往下的"牆",應該山頂有祭壇,有四條氣派通道上山到祭壇。 25/11/19 Upon the open grasslands of what is now Kazakhstan, there once stood a Bronze Age settlement that may have served as a center of exchange and power around 1600 BC. The settlement — called Semiyarka and nicknamed “The City of Seven Ravines” for its location overlooking a network of valleys — was first discovered in the early 2000s. What the team discovered was an expansive area that was once replete with houses, a central monumental building, which may have been used for rituals or governance, and possibly even tin bronze metal production facilities. Spanning 140 hectares (about 346 acres) above the Irtysh River (額爾齊斯河) valley, the large size and strategic location of the settlement may indicate that the Bronze Age steppe had sophisticated cities similar to those located in more urban areas of the world at the time. |
|
| ( 心情隨筆|雜記 ) |