字體:小 中 大
字體:小 中 大 |
|
|
|
| 2021/03/05 19:42:20瀏覽2090|回應0|推薦0 | |
第三章 Java程式語言的語法:資料型態與運算 語言的資料型態和運算。這可以說是每種程式語言重要基礎概念,本章的重點,
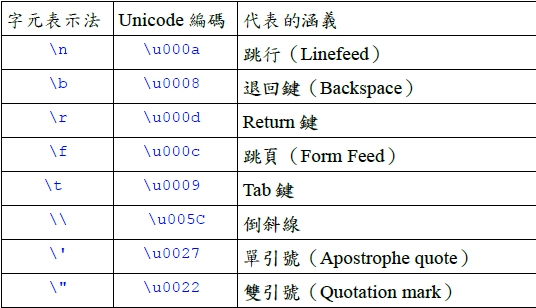
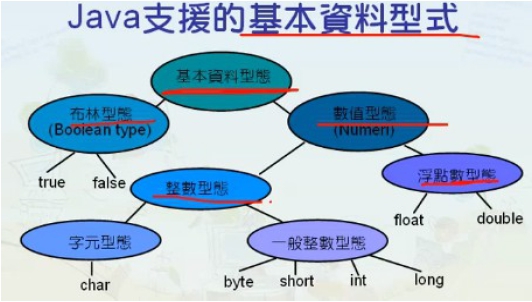
Java的基本值 單元目標: 初步認識Java的基本值。 對各種基本值的樣貌有正確的概念。 電腦表示資料的方法: 電腦的硬體使用0與1來表示資料。 01000001代表什麼?十進位的 65? 八進位的 101? 英文字母的A? 一張數位照片上的一個點? 電腦如何表示各種不同形式的資料? 現實世界的資料如何透過程式進行處理? Java的基本值簡介: 基本值就是常數。 程式中的資料表示法決定基本值所代表的意義:同一個基本值在不同的資料形態下所代表的意義會不一樣。 常見的幾種基本值形態:整數、浮點數。 字元、字串。 布林值。 整數常見的整數表示法: 十進位、八進位、二進位、十六進位。 Java支援的整數: 字元(Char)。 Byte。 Int。 short。 long。 浮點數 包含小數的數、科學符號表示法:如 1.56。 如 9E10 = 9x10¹⁰。Java的浮點數類型:float 單精度浮點數: 可大到約3.4E38。double倍精度浮點數。 字元 字元基本值常用單引號框起來,例如‘b’就代表字元b。字元在電腦中可以用16位元的Unicode編碼方式來表示,例如‘\u0041’代表‘A’。有些字元並不是常用的字元,或是無法在電腦鍵盤上找到的,仍然有對應的Unicode編碼。 特殊字元的 Unicode編碼
字串是一連串的字元的組合,在語法上是以雙引號將字串框起來:例如:“This is a string.” 就是一個字串。特殊字元也可以拿來組成字串:例如: “This message is from \”NOU\“. \u0009” 。 布林值 包含了true和false兩個基本值。使用兩個bytes來儲存,有些程式語言使用0與1 來代表布林值。Java中只能用保留字true與false來代表布林值。 特殊的基本值 空值(null value),指未指向任何位址的參考變數值。 空值和空白不一樣。 基本值表示法: 以整數來說,八進位和十六進位的表示法就利用0與0x 的前置字元來分辨進位法。如0x6c=6*16¹+12×16º=96+12=108。 Java裡的資料型式與變數: 認識Java中的變數。瞭解Java變數的類態。 Java裡的變數有三大類: 類別的成員(也稱為案例變數)。靜態成員(只屬於類別,不屬於特定的物件)。一般的變數(即宣告於方法中或是程式片段中的變數,也就是一般程式語言所指的變數)。 變數的內容: 變數具有一個名稱、型態、大小與所代表的值。宣告一個變數時,通常會指明這些成分。所謂的「物件參考」其實也是用值來表示的,所以有所謂的物件參考變數。這一類變數有一個很特別的地方,就是宣告時使用的是物件所屬的類別。物件參考儲存的值代表某個物件儲存空間的位址。
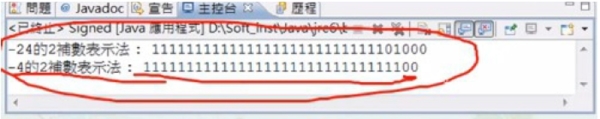
-4的2補數表示法 檔案 :Signed.java //-4的2補數表示法 class Signed { public static void main(String args[ ]) { String s = Integer.toBinaryString(-24); System.out.println("-24的2補數表示法 : " + s); String r = Integer.toBinaryString(-4); System.out.println("-4的2補數表示法 : " + r); } } 執行結果
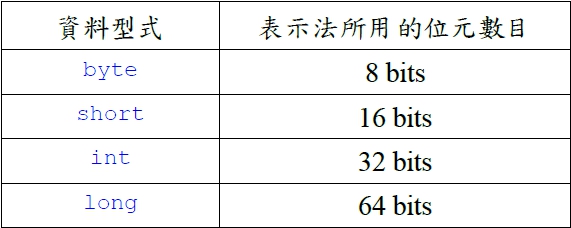
4 = 00000000000000000000000000000100 取2補數 = 11111111111111111111111111111011+1 = 11111111111111111111111111111100 Java的浮點數表示法: 以「超64為例」 把-255₁₀變成以2為基底的數值,同時要求用超 64法單精度實數來表示 -255₁₀=-11111111₂=-0.11111111×2⁸ 符號(1位):負值為1 指數(8位):8₁₀+64₁₀=72₁₀=01001000₂ 尾數(23位):11111111000000000000000₂ 所以最後得到的結果為:10100100011111111000000000000000₂ public class Signed { // -4的2補數表示法 public static void main(String args[ ]) { // Integer i = Integer.decode("0x80"); String s = Integer.toBinaryString(-24); System.out.println("-24的2補數表示法 : " + s); String r = Integer.toBinaryString(-4); System.out.println("-4的2補數表示法 : " + r); } } 執行結果 -24的2補數表示法 : 11111111111111111111111111101000 -4的2補數表示法 : 11111111111111111111111111111100 public class Signed { // -4的2補數表示法 public static void main(String args[ ]) { // Integer i = Integer.decode("0x80"); String s = Integer.toBinaryString(24); System.out.println("24的2補數表示法 : " + s); String r = Integer.toBinaryString(4); System.out.println("4的2補數表示法 : " + r); //String t=Integer.toBinaryString(i); //System.out.println("0x80的2補數表示法:" + t); //System.out.printf("0x80的10進位表示法: %d" i); } } 執行結果 24的2補數表示法 : 11000 前面的0在java裡都省略 4的2補數表示法 : 100 算術運算: 認識Java中的算術運算。學會使用+、-、*、/與%等算術運算子。 算術運算是最基本的運算之一。所有的程式語言都具備有這些運算功能。常見的算術運算子有: 加(+)、減(-)、乘(*)、除(/)、取餘數(%)。 public class Signed { // -4的2補數表示法 public static void main(String args[ ]) { Integer i = Integer.decode("0x80"); String s = Integer.toBinaryString(24); System.out.println("24的2補數表示法 : " + s); String r = Integer.toBinaryString(4); System.out.println("4的2補數表示法 : " + r); String t=Integer.toBinaryString(i); System.out.println("0x80的2補數表示法:" + t); //System.out.printf("0x80的10進位表示法: %d" i); } } 執行結果 24的2補數表示法 : 11000 4的2補數表示法 : 100 0x80的2補數表示法:10000000 public class Signed { // -4的2補數表示法 public static void main(String args[ ]) { Integer i = Integer.decode("0x80"); String s = Integer.toBinaryString(24); System.out.println("24的2補數表示法 : " + s); String r = Integer.toBinaryString(4); System.out.println("4的2補數表示法 : " + r); String t=Integer.toBinaryString(i); System.out.println("0x80的2補數表示法:" + t); System.out.printf("0x80的10進位表示法: %d", i); } } 執行結果 24的2補數表示法 : 11000 4的2補數表示法 : 100 0x80的2補數表示法:10000000 0x80的10進位表示法: 128 /加(+)、減(-)、乘(*)、除(/)和取餘數(%)的算術運算子 class iMath { public static void main(String args[]) { int x=20, y=9; System.out.println("顯示算術運算子的語法 : "); System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("y = " + y); System.out.println("x + y = " + (x + y)); System.out.println("x - y = " + (x - y)); System.out.println("x * y = " + (x * y)); System.out.println("x / y = " + (x / y)); System.out.println("x % y = " + (x % y)); } } 顯示算術運算子的語法 : x = 20 y = 9 x + y = 29 x - y = 11 x * y = 180 x / y = 2 x % y = 2 /加(+)、減(-)、乘(*)、除(/)和取餘數(%)的算術運算子 class iMath { public static void main(String args[]) { int x=24, y=9; System.out.println("顯示算術運算子的語法 : "); System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("y = " + y); System.out.println("x + y = " + (x + y)); System.out.println("x - y = " + (x - y)); System.out.println("x * y = " + (x * y)); System.out.println("x / y = " + (x / y)); System.out.println("x % y = " + (x % y)); } } 顯示算術運算子的語法 : x = 20 y = 9 x + y = 29 x - y = 11 x * y = 180 x / y = 2 x % y = 6 與位元相關的運算: 認識Java中的位元運算。學會使用「&」、「|」與「^」、「~」等位元運算子。 常見的位元運算子有: AND(&)、OR(|)、XOR(^)。 位元運算例 x=4₁₀=0100₂,y=5₁₀=0101₂ ,因此,計算的結果如下: 0100 AND 0101= 0100₂ = 4₁₀(要都為1,才得到1)0100 OR 0101 = 0101₂ = 5₁₀(任一方為1,即為1)0100 XOR 0101 = 0001₂ = 1₁₀(兩方不同值時得到) //位元運算 class Bit { public static void main(String args[]) { int x=4, y=5; System.out.println("顯示位元運算的語法 : "); System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("y = " + y); System.out.println("x & y = " + (x & y)); System.out.println("x | y = " + (x | y)); System.out.println("x ^ y = " + (x ^ y)); } } 執行結果 顯示位元運算的語法 : x = 4 y = 5 x & y = 4 x | y = 5 x ^ y = 1 「~」運算子會將0與1互換。 例: x=34₁₀=100010₂,將0與1互換之後, ~x=11…1011101₂,變成一個負數。由於2補數的緣故 34₁₀經過「~」運算變成-35₁₀。 class BitOP { public static void main(String args[]) { int x = 34; System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("x = " + Integer.toBinaryString(x)); int y = ~x; System.out.println("y = " + y); System.out.println("y = " + Integer.toBinaryString(y)); int a = 4; System.out.println("a = " + a); System.out.println("a = " + Integer.toBinaryString(a)); int b = ~a; System.out.println("b = " + b); System.out.println("b = " + Integer.toBinaryString(b)); } } 執行結果 X = 34 若x = -34 x = 100010 前面0位元省略,利用2補數法反轉成-35 x = 11111111111111111111111111011110 Y = -35 y = 33 Y = 11111111111111111111111111011101 y = 100001 a = 4 a = 100 b = -5 b = 11111111111111111111111111111011 資料型式的數值範圍: 瞭解Java中不同的資料型態使用的位元數目不同。 瞭解不同的資料型態其使用的位元數目與可表示的資料範圍的關係。 變數使用的位元數目: 為了充分發揮電腦儲存空間的使用效率,不同資料型態的變數會使用不一樣的位元數目來儲存。使用的位元數目愈大,可以表示的資料範圍也就愈大。 Java中的整數資料型式
想想看這些資料型式的表示範圍? class DataRange { public static void main(String arg[]) { int i = (int) (Math.pow(2,31)-1); System.out.println(" i = " + Integer.toBinaryString(i)); System.out.println("i = " + i); i=i+1; System.out.println("new i = " + i); System.out.println(" i = " + Integer.toBinaryString(i)); } } 執行結果 i = 1111111111111111111111111111111 2³¹-1的2進位表示法 i = 2147483647 2³¹-1的10進位表示法 new i = -2147483648 溢位, 反轉為負的最大值(2補數法) i = 10000000000000000000000000000000 -2³¹ Java中的浮點數資料型式
想想看這些資料型式的表示範圍? 運算子的特殊用法: 瞭解Java中++與—等特殊運算子,並能分辨出其出現在變數前與變數後的差別。學會移動位元的運算子。 ++與--運算: 運算子「++」可使變數累加1。運算子「--」可使變數累減1。「++」和「--」放在變數的前方會先執行累加或累減運算,再執行包含「++」和「--」的敘述。 class AddSubOne { public static void main(String args[]) { int x = 8, y = 13; System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("y = " + y); System.out.println("++x = " + ++x); System.out.println("y++ = " + y++); System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("y = " + y); } } 執行結果 x = 8 y = 13 ++x = 9 y++ = 13 x = 9 y = 14 移動位元的運算子: 「<<」運算子把位元往左平移。「>>>」和「>>」都代表往右平移。 兩者的差別在於:「>>」在平移時不影響決定正負號的位元(即最左邊的位元)。 「>>>」在平移時不管是什麼位元,往右平移後,左邊空出來的位置一律填入0。 「<<」例: 例如「a<<2 font="">」代表將變數a的值所對應的位元組往左平移2個位元。 假如a的值是7,則往左平移的操作可以用下面式子說明: a=7₁₀=111₂ 往左平移2位後得到 11100₂=28₁₀ class Shift { public static void main(String args[]) { int x = 5; System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("x >> 2 = " + ( x >> 2)); System.out.println("x << 1 = " + ( x << 1)); System.out.println("x >>> 1 = " + (x >>> 1)); } } 執行結果 x = 5 x >> 2 = 1 x << 1 = 10 x >>> 1 = 2 邏輯運算: 認識基本值True、False與邏輯運算的關係。瞭解Java中的邏輯運算:關聯運算子、布林運算子。 邏輯運算的基本值: 寫程式時還經常用到一些決定與「是」與「否」的情況,在基本值中我們用「真」True與「假」False來支援這一類的需求,其實就是所謂的「布林」資料型式。 關聯運算子,運算的結果就是「真」或「假」,亦即一般人常稱的「邏輯」運算。布林運算子的運算元與運算結果都是True或False。 關聯運算子的涵義
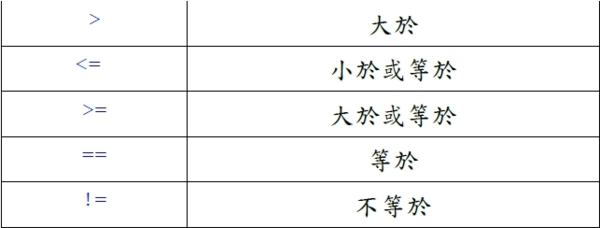
class RelOP { public static void main(String args[]) { int x = 2, y = 63, z = 34; System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("y = " + y); System.out.println("z = " + z); System.out.println("x < y = " + (x < y)); System.out.println("x > z = " + (x > z)); System.out.println("y <= z="" 000000="" y="" font="" span="" p="" style="font-size:8pt" color="#2a00ff" face="Courier New, monospace" size="1" system="" i="" out="" println="" x="" data-mce-style="font-size: 8pt;">= y = " + (x >= y)); System.out.println("y == z = " + (y == z)); System.out.println("x != z = " + (x != z)); } } 執行結果 x = 2 y = 63 z = 34 x < y = true x > z = false y <= z="false</span"> x >= y = false y == z = false x != z = true 布林運算子
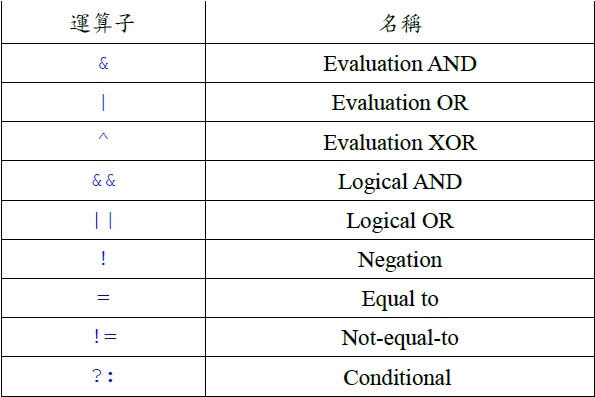
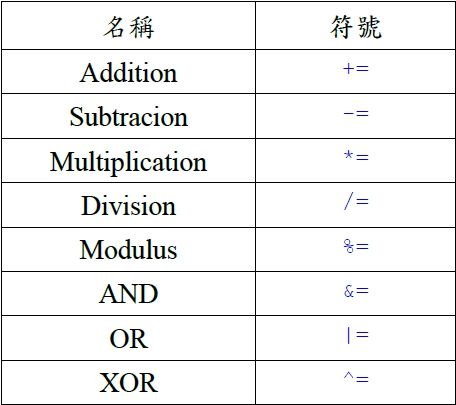
Evaluation與Logical的差別: boolean pass=isLegal &(attendant>100);boolean pass=isLegal && (attendant>100);第一行中,兩邊的運算式都要先取值(evaluate),再以&來求值。 第二行則先求isLegal的值,假如已能決定結果,就不再求取&&右邊運算式的值。 從程式語言處理的效率來看,顯示後者的處理方式比較占優勢。 ?: 運算子: ?:是三方(Ternary)運算子。用法很特殊,例如:a = isOld ? 60 : 7; 代表若是isOld的值為真,則a=60。若isOld的值為假(False),則a=7。 也就是說,「?」前面的布林值為真時,「?」右邊的運算式為整個運算式的值,否則以「:」右方的運算式當成整個運算式的值。 字串的連結與特殊的運算子: 認識字串連結運算子 +。認識改變整數正負號運算子–。認識特殊的指定值運算子。 字串連結運算子+ : + 是算術運算中的加法運算,用於字串時則成為字串連結運算子。 改變整數正負號運算子-: -是算術運算中的減法運算,單獨用於一個數字前則成為改變整數正負號運算子(一元運算子)。 class Concat { public static void main(String args[]) { String front = "Where " + "is "; String rear = "Missouri " + "State?"; System.out.println(front + rear); System.out.println("This" + " is" + " another" + " way. "); } } Where is Missouri State? This is another way. class Neg { public static void main(String args[]) { int x = 123; System.out.println("x = " + x); int y = -x; System.out.println("y = " + y); } } x = 123 y = -123 指定值運算子: Java和C++類似,提供了簡化程式寫法的語法,讓程式寫作更精簡:例如:a*=(b+4);代表a=a*(b+4); a+=2 ;代表a=a+2 ; 指定值運算子列表
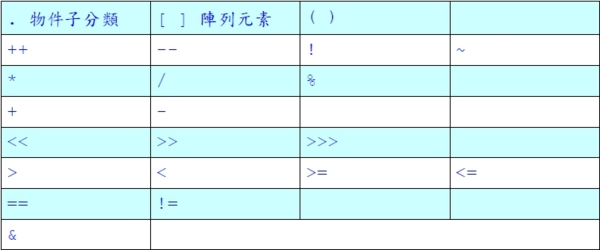
運算子處理的優先順序: 瞭解Java中各種運算子的處理優先順序。 程式中,一個敘述可能包含很長的運算式,其中有各種運算子,這時候那個運算子要先處理,需有一定的規則,否則無法正確得到執行的結果。我們把這樣的規則稱做優先順序。例如:1*2+3*4。先乘除後加減是一般算術的運算順序。Java中包含各式的運算子,程式設計者必須知道各運算子的優先順序,才能避免發生錯誤。
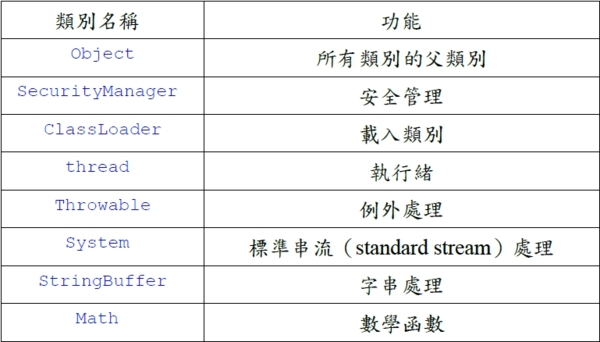
奇特的Object類別: 瞭解Java是物件導向語言。 認識Java類別觀念與基本類別。 Java物件導向觀念: Java是物件導向語言。Java程式對於資料處理是以類別的觀念為核心。 要寫出複雜而功能豐富的Java程式,除了要對語法有深入的了解之外,也要多認識一些現成而有用的類別。 java.lang包裹裡含有重要的基本類別:每個 Java程式在編譯時都自動引入 java.lang包裹,因為一些一定要用到的類別都在這個包裹中。 java.lang裡的重要類別
Object類別: Object 類別是所有Java類別的父類別。 Object 類別具有所有類別的共同特徵,同時也提供了一些好用的方法。
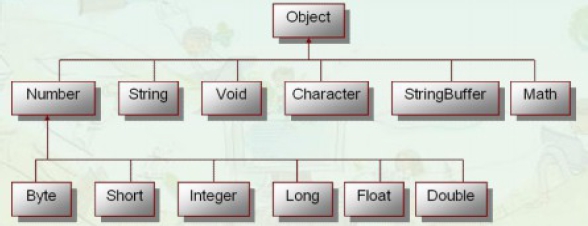
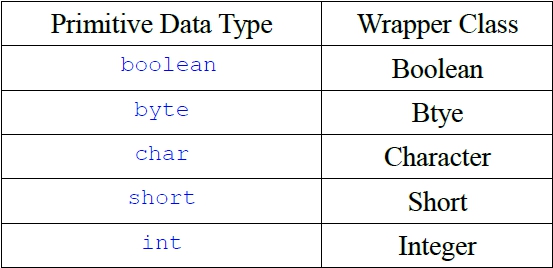
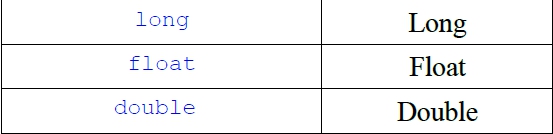
包裝類別: 瞭解在Java中建構物件的方法。 認識包裝類別的相關方法與常數、函數。 基本資料型態與包裝類別: 於8種基本資料型態,會有對應的類別,稱為包裝類別. 這些包裝類別已寫好常用的方法,而且提供許多靜態的方法。屬於8種基本資料型態之變數,不需new,集可以在宣告使用,如int i ;屬於包裝類別資料型態之變數為物件,需new,才可以使用 如Integer i=new Integer();
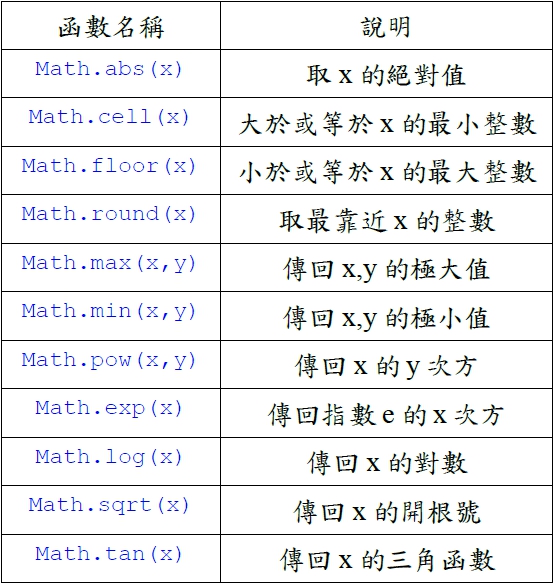
建構物件的方法: 在物件導向系統,所有的事物或觀念都可看成是物件。 每一種基本資料型式都包含一個對應的包裝類別,其建構物件的方式可用。 Boolean boolObj = new Boolean(true); 資料型式物件名稱 基本值 或Boolean boolObj = new Boolean(“true”); 包裝類別方法與常數: 和包裝類別有關的方法,像valueOf( )、tostring( )。 Boolean boolObj2 = Boolean.valueOf("false"); String boolstr = boolObj2.tostring( ); // 得到 false 字串 boolean boolVar = boolObj2.booleanValue( ); // false 指定給 boolVar int m = intobj.intValue(312); // 312指定給變數 m boolean objComp = boolObj.equals(boolObj2); 包裝類別定義了一些常數:Boolean.TRUE、Boolean.FALSE、character.MIN_VALUE、character.MAX_VALUE等。 對於數值來說,可以用parseByte( )、parseInt( )、parseDouble( )直接把字串參數轉換成數值。 好用的數學函數: 認識在Java中的數學函數。 學會在程式中應用數學函數。 Math類別中的函數: java.lang中的Math類別提供很多數學函數,讓我們很方便地用Java語言來表示各種數學式。 重要的數學常數: Math.E // 代表自然對數(natural logarithm)的底(base)。 Math.PI // 即三角函數裡常用的圓周率。 常見的數學函數:
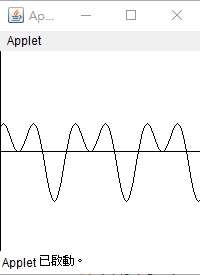
數學函數實例: class AboutMath { public static void main(String args[]) { long a = Math.abs(-129); double b = Math.abs(-Math.PI); double c = Math.ceil(Math.PI); double d = Math.floor(Math.PI); long e = Math.round(Math.PI); long f = Math.max(1253L, 3214L); double g = Math.min(Math.PI, Math.E); double h = Math.pow(3.0,2.0); double i = Math.exp(3.0); double j = Math.log(Math.E); double k = Math.sqrt(3.0*3.0+4.0*4.0); double l = Math.tan(Math.PI/4.0); System.out.println("a= " + a + " b=" + b + " c=" +c); System.out.println("d= " + d + " e=" + e + " f=" +f); System.out.println("g= " + g + " h=" + h + " i=" +i); System.out.println("j= " + j + " k=" + k + " l=" +l); System.out.println("random numer: "); for (int m=1; m<=5; m="" font=""> System.out.println(Math.random()*m); } } 執行結果 a= 129 b=3.141592653589793 c=4.0 d= 3.0 e=3 f=3214 g= 2.718281828459045 h=9.0 i=20.085536923187668 j= 1.0 k=5.0 l=0.9999999999999999 random numer: 0.19165421969292473 1.6854751963476589 2.6816790895718956 0.0055188067723821455 3.718146759262793 三角函數畫圖: import java.applet.*; import java.awt.*; public class drawf extends Applet { int a,b,x,y; int amplitude(int x) { y=a/2-(int)(a/50*Math.cos(2*x*Math.PI/36) ); return y; } public void paint(Graphics g) { a=getSize().width; b=getSize().height; g.drawLine(0,a/2,b,a/2); g.drawLine(0,0,0,a); for (int x=0; x<b;x++) { g.drawLine(x,amplitude(x),x+1,amplitude(x+1)); } } } 執行結果
請撰寫一個 Java Applet 程式,可以繪製y=a/2-a/8(sin(πx/36)+cos(2πx/36))函數圖形。 import java.applet.*; import java.awt.*; public class drawf extends Applet { int a,b,x,y; int amplitude(int x) { y=a/2-(int)(a/8*Math.sin(x*Math.PI/36)+Math.cos(2*x*Math.PI/36) )); return y; } public void paint(Graphics g) { a=getSize().width; b=getSize().height; g.drawLine(0,a/2,b,a/2); g.drawLine(0,0,0,a); for (int x=0; x<b;x++) { g.drawLine(x,amplitude(x),x+1,amplitude(x+1)); } } }
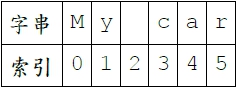
字串處理的複雜功能: 認識在Java中的字元與字串的概念。 認識字串函數與其應用。 字串可看成是由字元組成的陣列。 字串中各字元都有一個對應的索引。 例:
相關函數: length()可以傳回字串的長度。 charAt()方法可以直接引用字串中某個位置的字元。 equals()方法可比較字串, true代表相同。 compartTo()可比較字串的大小。 indexOf()可以傳回子字串所在的位置。 trim()可將字串前後的空白清除。 class aboutString { public static void main(String args[ ]) { String str = "My own car costs $20000!"; // int length() 和 char charAt(int index)的用法 System.out.println(str.charAt(str.length()-1)); String str2="Your car costs $23000!"; System.out.println("str = str2 ?" + str.equals(str2)); System.out.println("str = str2 ?" + str.compareTo(str2)); // 搜尋子字串 (substring) String substr="costs"; System.out.println("costs located at " + str.indexOf("costs")); System.out.println("Trimmed str : " + str.trim()); System.out.println("string conversion : " + String.valueOf(true)); System.out.println("string conversion : " + String.valueOf(new char[] {d,3})); } } 執行結果 ! str = str2 ?false str = str2 ?-12 costs located at 11 Trimmed str : My own car costs $20000! string conversion : true string conversion : d3 有彈性的字串處理功能: 瞭解StringBuffer類別的功能。 學會應用StringBuffer類別中的函數處理字串。 StringBuffer 類別: String 類別對於字串的處理不包括對字串內容的改變。 假如要改變字串的內容,可使用StringBuffer類別。 StringBuffer可看成是一個字串處理的緩衝區。 StringBuffer應用宣告:宣告的時候,可指定字串處理單元的大小 例如:stringBuffer strBuf = new stringBuffer(15) ; 相關函數:直接改變字串中某個字元的內容,可用setcharAt( ), 指定更改後的值,以及該字元所在的索引位置。完成字串的處理之後,可將緩衝區內的值變成(或指定給)一般的字串變數,所用的方法是tostring() 。 delete()、insert( )和append() 可用來對字串進行刪除、插入和由後加入的處理。 class aboutStringBuffer { public static void main(String args[]) { StringBuffer strBuf = new StringBuffer("Hi folks!"); System.out.println("1. strBuf = " + strBuf); strBuf.setCharAt(strBuf.length()-1, .); System.out.println("2. strBuf = " + strBuf); String myStr=strBuf.toString(); strBuf = strBuf.delete(2,9); System.out.println("3. strBuf = " + strBuf); strBuf=strBuf.append(" dear!"); System.out.println("4. strBuf = " + strBuf); strBuf=strBuf.insert(3,"my "); System.out.println("5. strBuf = " + strBuf); System.out.println("6. strBuf = " + strBuf.reverse()); } } 1. strBuf = Hi folks! 2. strBuf = Hi folks. 3. strBuf = Hi 4. strBuf = Hi dear! 5. strBuf = Hi my dear! class aboutStringBuffer { public static void main(String args[]) { StringBuffer strBuf = new StringBuffer("Hi folks!"); System.out.println("1. strBuf = " + strBuf); strBuf.setCharAt(0, .); System.out.println("2. strBuf = " + strBuf); String myStr=strBuf.toString(); strBuf = strBuf.delete(2,9); System.out.println("3. strBuf = " + strBuf); strBuf=strBuf.append(" dear!"); System.out.println("4. strBuf = " + strBuf); strBuf=strBuf.insert(3,"my "); System.out.println("5. strBuf = " + strBuf); System.out.println("6. strBuf = " + strBuf.reverse()); } } 1. strBuf = Hi folks! 2. strBuf = .i folks! 3. strBuf = .i 4. strBuf = .i dear! 5. strBuf = .i my dear! 自訂資料輸入類別: 學會撰寫類別方法。 學會從鍵盤讀取各種資料並進行處理。 讀取使用者輸入的值 目標:撰寫一個通用的程式可以讀取各種資料。 思考重點: 提供一個buffer reader讀取鍵盤輸入值。 提供各種資料型態的處理方法。 整數 (int)。 長整數 (long)。 倍準實數 (double)。 一般實數 (float)。 字元 (char)。 字串 (string)。 同一時間對於同一物件而言,只有一個方法執行。 使用 buffer reader 讀取鍵盤輸入: private final BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader (System.in)); 把輸入值當成整數資料 public final synchronized int getInteger() { String usrInput = "" ; int rvalue = 0 ; try { usrInput = in.readLine() ; } catch (IOException e) { } if (usrInput != null) { try { rvalue = Integer.parseInt(usrInput) ; } catch (NumberFormatException e) { } } return rvalue; } 把輸入值當成長整數資料 public final synchronized long getLong() { String usrInput = "" ; long rvalue = 0L ; try { usrInput = in.readLine() ; } catch (IOException e) { } if (usrInput != null) { try { rvalue = Long.parseLong(usrInput) ; } catch (NumberFormatException e) { } } return rvalue; } 把輸入值當成倍準實數資料 public final synchronized double getDouble() { String usrInput = "" ; double rvalue = 0.0D ; try { usrInput = in.readLine() ; } catch (IOException e) { } if (usrInput != null) { try { rvalue = Double.parseDouble(usrInput) ; } catch (NumberFormatException e) { } } return rvalue; } 把輸入值當成一般實數資料 public final synchronized float getFloat() { String usrInput = "" ; float rvalue = 0.0F ; try { usrInput = in.readLine() ; } catch (IOException e) { } if (usrInput != null) { try { rvalue = Float.parseFloat(usrInput) ; } catch (NumberFormatException e) { } } return rvalue; } 把輸入值當成字元資料 public final synchronized char getCharacter() { char rvalue = ; try { rvalue = (char)in.read(); in.readLine(); //以免影響下面的輸入 } catch (IOException e) { } return rvalue; } 把輸入值當成字串資料 public final synchronized String getString() { String rvalue = "" ; try { rvalue = in.read(); } catch (IOException e) { } if (rvalue == null) { rvalue = "" ; } return rvalue } 自訂資料輸入類別應用: 學會撰寫測試各種輸入的程式。 學會撰寫簡單的應用程式。 測試讀取使用者輸入的值 public static void main(final String[ ] args) { GetUsrInput in = new GetUsrInput() ; System.out.print("請輸入一個整數: ") ; int usr_n = in.getInteger() ; System.out.println("輸入的整數值為: " + usr_n) ; System.out.print("請輸入一個長整數: ") ; long usr_l = in.getLong() ; System.out.println("輸入的長整數值為: " + usr_l) ; System.out.print("請輸入一個倍準實數: ") ; double usr_d = in.getDouble() ; System.out.println("輸入的倍準實數值為: " + usr_d) ; System.out.print("請輸入一個實數: ") ; float usr_f = in.getFloat() ; System.out.println("輸入的實數值為: " + usr_f) ; System.out.print("請輸入一個字元: ") ; char usr_c = in.getCharacter() ; System.out.println("輸入的字元值為: " + usr_c) ; System.out.print("請輸入一個字串: ") ; String usr_s = in.getString() ; System.out.println("輸入的字串值為: " + usr_s) ; } } 撰寫簡單應用程式 功能: 輸入要平均的數字個數。 依次輸入數字。 計算出平均。 列印出平均。 輸入數字 import java.io.*; public class Cavg { double [ ] inum() { GetUsrInput in = new GetUsrInput( ); System.out.print("請輸入要平均的數值有幾個: "); int cc = in.getInteger(); double [ ] dnum = new double[cc]; for (int i=0; i System.out.print("請輸入要平均的第"+ (i+1) + "數值"); dnum[i] = in.getDouble(); } return dnum; } double cavg(final double [ ] dnum) { double sum = 0.0; for (int n = 0; nlength; ++n) { sum+=dnum[n]; } return sum/dnum.length; } public static void main(final String [ ] args) { Cavg oo = new Cavg(); double Cavg = oo.cavg(oo.inum( )); System.out.println("得到的平均為 : " + Cavg); } } 本章的內容很多、很細,學起來其實是相當辛苦的。請大家要多花一點時間在這個章節中。 第一節中的內容難度不高,應該可以容易完成,第二節中有關一些運算子的特殊用法、還有邏輯運算等,算是比較少會接觸到的內容,必須要多加強實務操作。 第三節的包裝類別,看似很抽象,其實如果學會了之後,光使用Java本身提供給我們的類別就有許多的便利功能在其中。 GetUsrInput中每一個函數定義的方式都類似,拆解開來看就容易理解了。此外,也還得搭配後面的UsrInputTest才能發揮效果。而第三個程式Cavg則是一個具體的綜合應用。 |
|
| ( 知識學習|隨堂筆記 ) |