字體:小 中 大
字體:小 中 大 |
|
|
|
| 2019/09/21 12:22:14瀏覽991|回應1|推薦4 | |
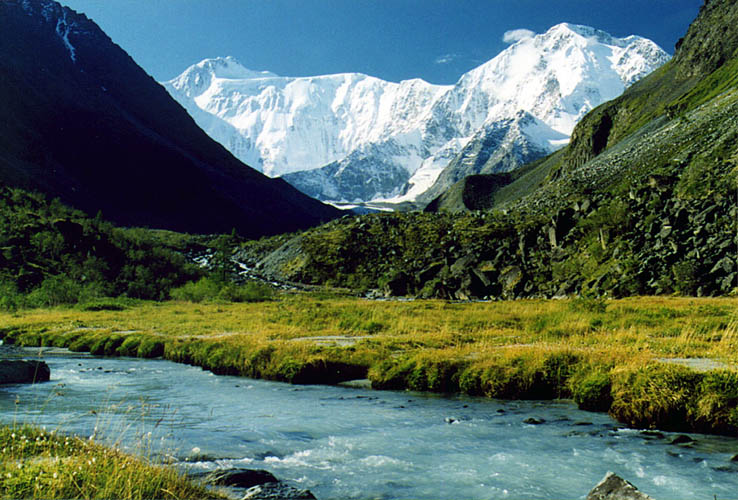
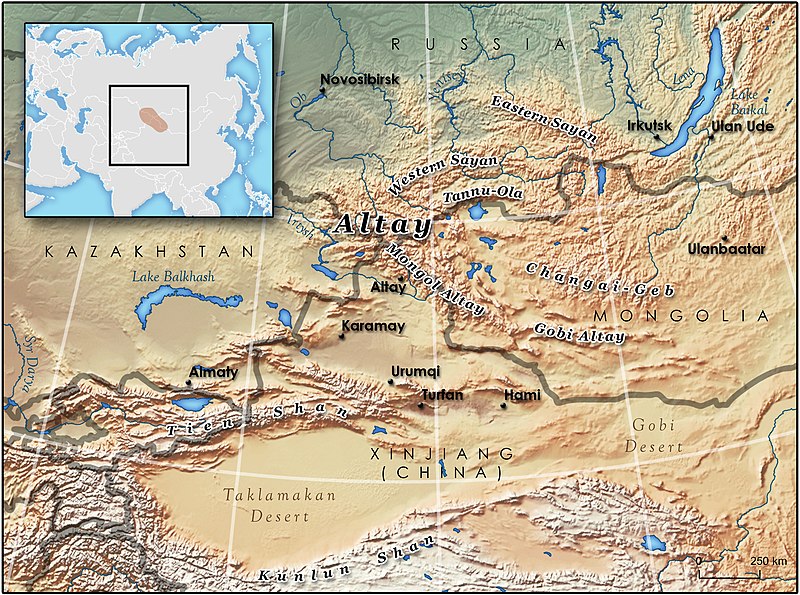
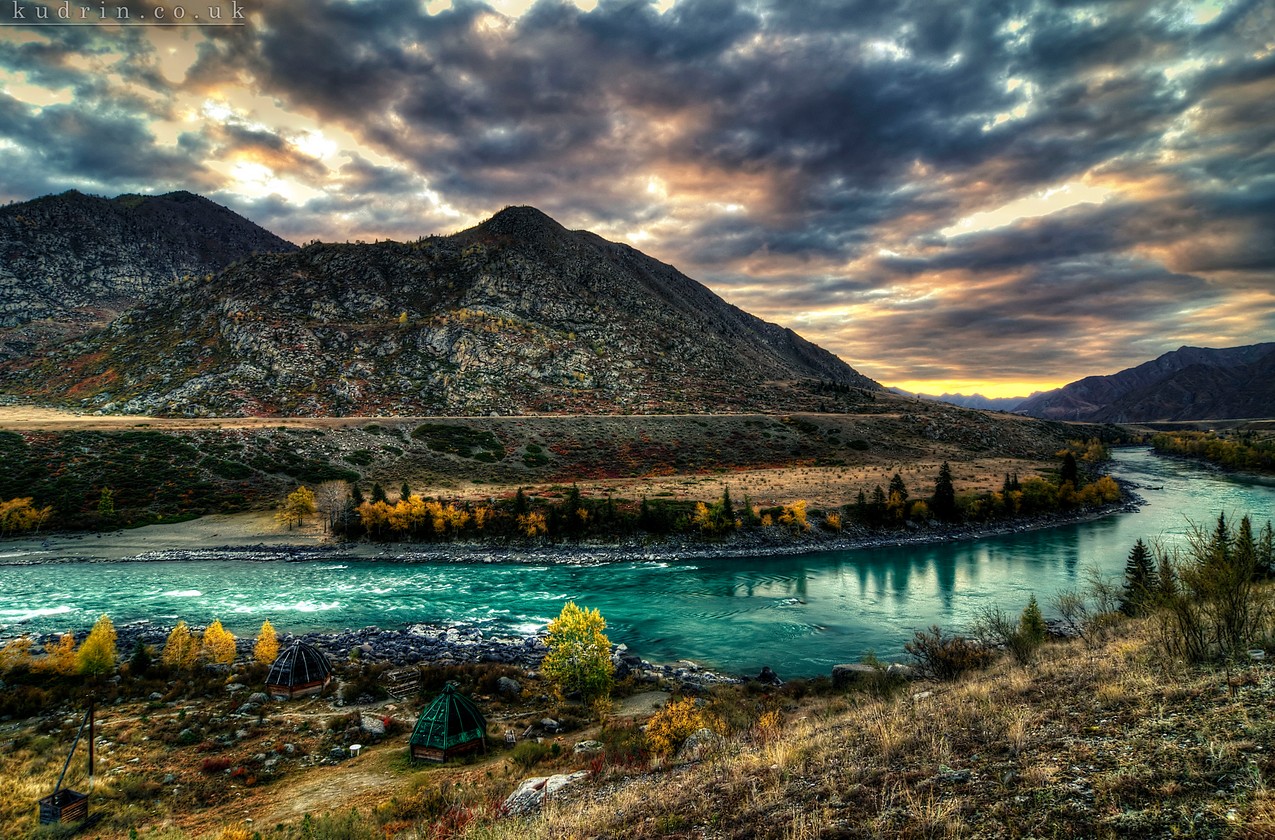
阿爾泰山脈(維吾爾語:ئالتاي تاغ تىزمىسى;俄語:Алтай;蒙古語:ᠠᠯᠲᠠᠢ ‧ Алтай或ᠠᠯᠲᠠᠢ
阿爾泰山脈幅員遼闊橫越俄羅斯,蒙古,中國,其中位於蒙古境內多處山區已開放旅遊,探險,以確保蒙古國的外匯收入,至於中國境內的阿爾泰山區,依然由維吾爾的少數游牧部落掌握管理,為天然的牧場逐水草而居. 有關俄羅斯境內的阿爾泰山區,幾乎是管制進入,這樣一來維持天然的景觀,是好的由於交通不便,人跡和罕見,生態環境保持良好,俄羅斯當局嚴禁狩獵,盜伐樹木及探勘採礦.,尤其以西方人的學術探勘隊或是以環境生態考察之名旅遊探險,阿爾泰山脈都是拒絕.
The Altai Mountains (/ɑːlˈtaɪ/), also spelled Altay Mountains, are a mountain range in Central and East Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia, and Kazakhstan come together, and where the rivers Irtysh and Ob have their headwaters. The massif merges with the Sayan Mountains in the northeast, and gradually becomes lower in the southeast, where it merges into the high plateau of the Gobi Desert. It spans from about 45° to 52° N and from about 84° to 99° E. The region is inhabited by a sparse but ethnically diverse population, including Russians, Kazakhs, Altais, and Mongolians. The local economy is based on bovine, sheep, and horse husbandry, agriculture, forestry, and mining. The now-disputed Altaic language family takes its name from this mountain range.
The five highest mountains of the Altai are:
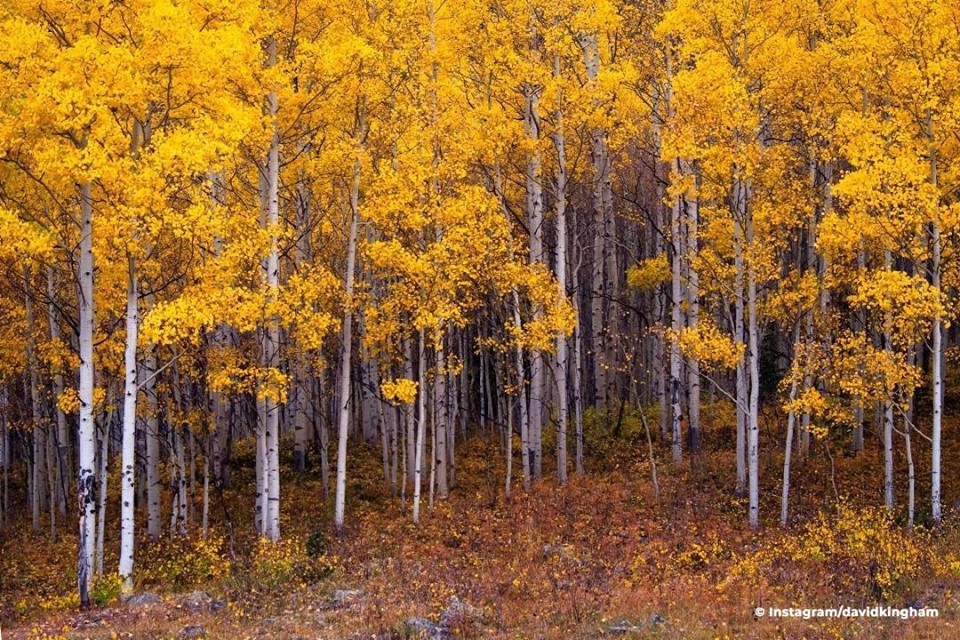
Autumn is a season of intensive work for Mongolians. As the sayings go “autumn arrives the day after the Naadam festival,” and “make hay while the sun shines”. Autumn for the Mongolians means to prepare for the winter.
|
|
| ( 休閒生活|旅人手札 ) |






 .
.