字體:小 中 大
字體:小 中 大 |
|
|
|
| 2017/03/07 13:15:25瀏覽750|回應2|推薦6 | |
|
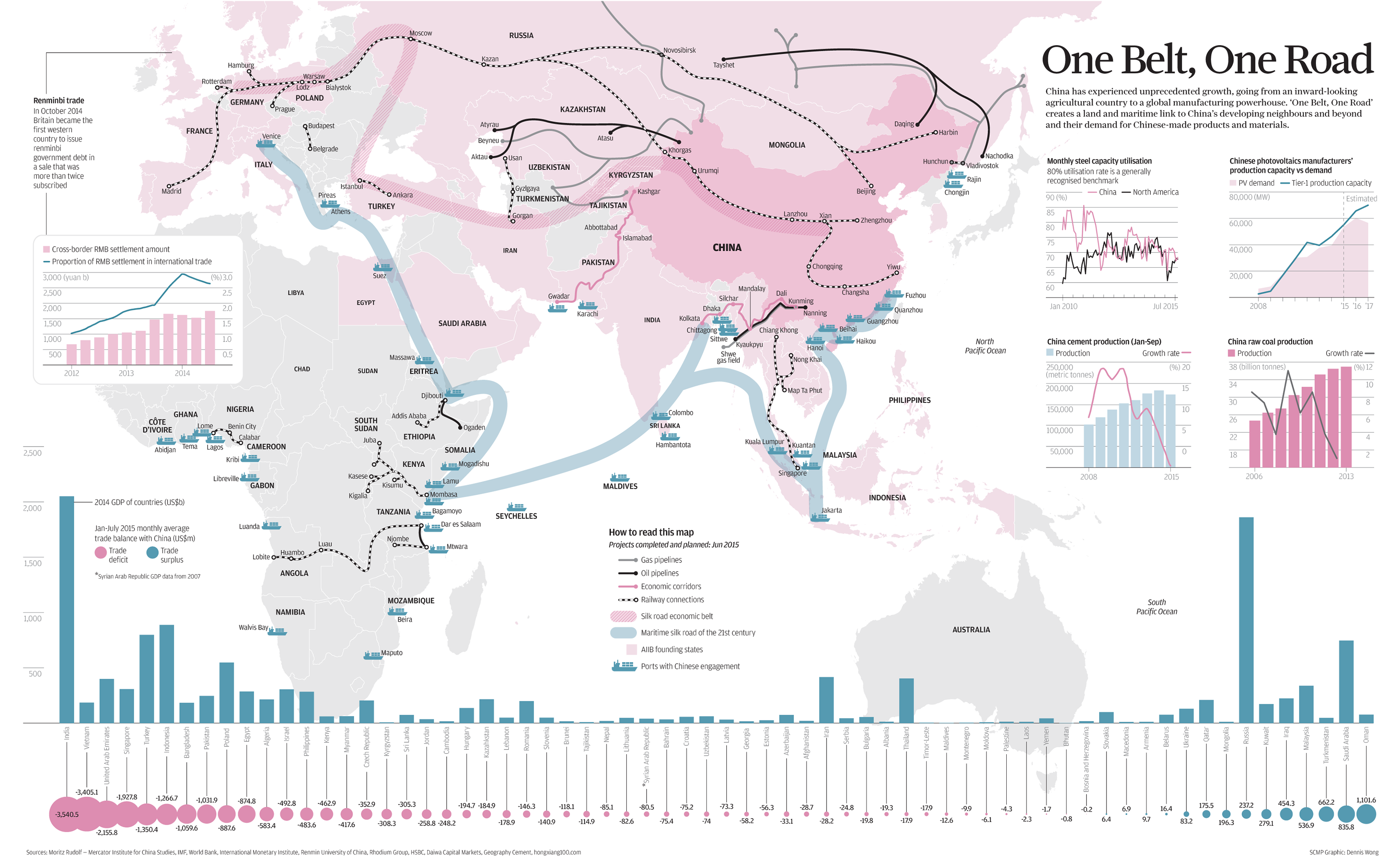
China To Build “Silk Road” For Project Finance.? China's "One Belt, One Road" intiative challenges existing project-financing banks for new Asian development. China’s “One Belt, One Road” (OBOR) initiative is the most ambitious overarching infrastructure project to be proposed in the modern era. OBOR, which was unveiled in 2013 and is the brainchild of China’s president Xi Jinping, aims to connect China with more than 60 countries—stretching from Western and Central Europe to East Africa and including South East Asia, the Middle East and Russia—via infrastructure development as well as trade and cultural exchange.
Also referred to as the New Silk Road project—a reference to the route by which ancient China traded with the West—the proposal has drawn comparisons with the Marshall Plan, which was instrumental in rebuilding Europe after World War II. But it is more ambitious: various estimates put OBOR’s scale, adjusted for inflation, at ten to 30 times the Marshall Plan; upon successful completion it will touch the lives of more than half the global population. No concrete timeline for completion has been stated. 中國建設“絲綢之路”項目融資:中國的“一帶一路”對新興亞洲發展項目融資銀行提出了挑戰。 到時2077-2107.的時期OBOR的沿線國家平均GNP已達20000 美元,屆時歐,美,日,已是窮途末路的窮鄉僻壤?
世界的重心轉移至此OBOR,當然幕後功臣就是中國,受益最多也是中國,因為2049年時期左右,中國已可能完全取代美國,成為國際貿易,軍事第一大國?除非發生第3次世界大戰否則按照時間表的計劃推動執行OBOR的作業將持續進行至22世紀.
Infrastructure: Can It Rebuild The Global Economy? 基礎建設可以重建全球經濟?
中國瘋狂: 此外,為了推動一帶一路,中國在2014年成立了絲綢之路基金,由國家外匯管理局,中國投資公司,中國進出口銀行和國家開發銀行贊助,資金總額為400億美元專門用於資助與一級方案有關的項目。一帶一路是共享繁榮的另一個因素。有必要進一步推動中國和作為”一帶一路“項目一部分的許多國家的公私伙伴關係框架。必須對項目進行公開招標,由於日本不是亞投行AIIB的會員國,所以沒有資格參與亞投行的各項公開招標的商業機會,但是日本3大重工業集團MHI.IHI.KHI.也正卯足全力,透過亞開行ADB的實力,進行與AIIB會員國私下接觸,並期望中標工程的國家提供機會,採購日本製造的基礎建設的機具設備,根據日本商社蒐集的商業資料顯示出,日本3大重工業集團仍有可望贏得20%的轉定單合約,但是首要條件是日商提供低利融資,由來已久日本重工業低迷不振,看樣子日本政府也只好睜隻眼閉隻眼由日本商社發展業務,因為無魚蝦也好不是嗎?
資本市場的初步反應令人鼓舞,並且正在開始從頭開始創建一個新的資產類別:“絲綢之路”標籤下的債券和貸款。中國提出了一個針對該品牌發行債券的獨立交易和結算系統。 目前,絲綢之路項目由中國領先的政策銀行雙邊貸款支配。當然,在邊際上,中國和地區商業銀行總是有機會參與聯合,甚至是項目債券,“Chander說。 “但是項目融資團隊和其他投資者在投入大量資金之前將非常仔細地評估風險回報曲線。
CHINA FLEXES ITS MUSCLES:China aims to counter the dominance of the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund in international development banking through the establishment of the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) and the New Development Bank, headquartered in Beijing and Shanghai, respectively. Both became fully operational last year with China as a major shareholder: 26.06% of the votes in the AIIB—where China effectively calls the shots on investment strategy within its borders—and 20% in the NDB. In addition, in seeking to boost OBOR, China in 2014 established the Silk Road Fund under the auspices of the State Administration of Foreign Exchange, China Investment Corporation, Export-Import Bank of China and China Development Bank, with total capital of US$40 billion earmarked for financing OBOR-related projects. “Adding the ‘Silk Road’ label to a debt-financing exercise can give it more focus and attention from investors due to the publicity already garnered by the Silk Road initiative,” says Clifford Lee, head of debt capital markets at DBS Bank in Singapore. At the same time, he adds, “the impact that this will have on the Asian project-finance market will depend more on the actual feasible project-finance opportunities that can surface from this initiative.” |
|
| ( 時事評論|財經 ) |